Interface¶
Interface configuration lets you change how UI elements are displayed and how they react.
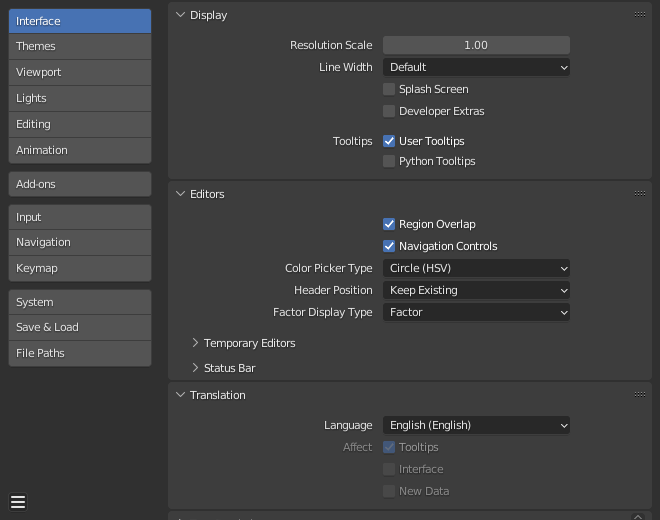
Display¶
- Resolution Scale
Adjusts the size of fonts and buttons relative to the automatically detected DPI. During typical usage, you may prefer to use zoom which is available in many parts of Blender interface.
- Line Width
Scale of lines and points in the interface e.g. button outlines, edges and vertex points in the 3D Viewport.
Thin, Default, Thick
- Splash Screen
Display the Splash Screen when starting Blender.
- Developer Extras
Show settings and menu items which are intended to help developers, this includes:
- Button Context Menu
- Online Python Reference
To open the Python reference manual.
- Copy Python Command
To copy the expression used when pressing the button.
- Edit Source
To edit Python source code that defines the button.
- Edit Translation
The option to edit UI translations (only available when the Manage UI translations add-on is also enabled).
- 3D Viewport
- Show Indices
The option to show mesh vertex/edge/face indices in the overlay popover.
- Preferences
- Experimental Tab
Work in progress features can be enabled here which are currently being tested.
- Tooltips
- User Tooltips
When enabled, a tooltip will appear when your mouse pointer is over a control. This tip explains the function of what is under the pointer, shows the associated hotkey (if any).
- Python Tooltips
Displays a property’s Python information below the tooltip.
- Search – Sort by Most Recent
Show most recently selected items at the top of search results, otherwise search results are sorted alphabetically.
Editors¶
- Region Overlap
This makes regions overlap the viewport. It means that the Toolbar and Sidebar regions, will be displayed overlapping the main area.
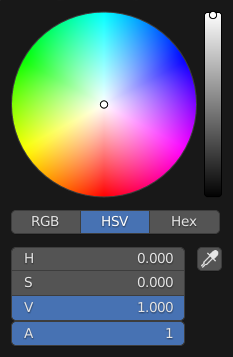
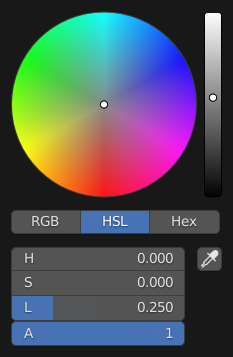
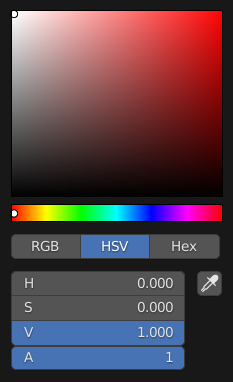
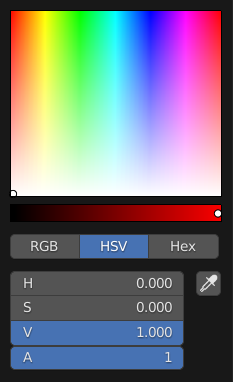
- Color Picker Type
Choose which type of Color Space you prefer for the Color picker. It will show when clicking LMB on any color field.
- Header Position
The default header position when opening a new editor.
- Keep Existing:
Uses top for most editor types and the positions saved in the start-up file.
- Top/Bottom:
Always positions the header at the top or the bottom of the editor.
- Factor Display Type
How factor value types are displayed in the user interface.
- Factor:
Values are displayed as float numbers between 0.0 and 1.0.
- Percentage:
Values are expressed as a percentage between 0 and 100.
Temporary Editors¶
When performing certain operations, Blender will open a new window. The behavior of these operations can be configured here.
- Render In
When rendering, the user interface can do any of:
- Keep User Interface:
The user interface does not change and the render is computed in the background.
- Maximize Area:
A new Image editor is opened as a temporary window in full screen mode.
- Image Editor:
The area that is the largest on screen is replaced placed by a temporary Image editor.
- New Window:
A new Image editor is opened as a regularly sized temporary window.
- File Browser
When opening files from the computer, the user interface can do any of:
- Maximize Area:
A new File Browser editor is opened as a temporary window in full screen mode.
- New Window:
A new File Browser editor is opened as a regularly sized temporary window.
Status Bar¶
Preferences that affect the Status Bar.
Show
- Scene Statistics
Shows information about the data in the active scene.
Collection: The name of the active Collection.
Active Object: The name of the active selected object.
Geometry: Information about the current scene depending on the mode and object type. This can be the number of vertices, faces, triangles, or bones.
Objects: The number of selected objects and the total count of objects.
- Scene Duration
Shows the total amount of time of the playback along with the current frame number and total frame count. The format of the duration text is determined by the Timecode Style.
- System Memory
Shows an estimate of Blender’s RAM consumption. On a single-instance single-machine scenario, this estimate provides a measurement against the hardware limit of the machine.
- Extensions Updates
Shows the number of extensions with available updates.
- Blender Version
Shows the version number of Blender that is currently running.
Language¶
- Language
The language used for translating the user interface (UI). The list is broken up into categories determining how complete the translations are.
- Translate
- Tooltips
Translates the descriptions when hovering over UI elements.
- Interface
Translates all labels in menus, buttons, and panels.
- New Data
Translates the names of new data-blocks.
Text Rendering¶
- Anti-Aliasing
Enable interface text Anti-Aliasing. When disabled, texts are rendered using straight text rendering (filling only absolute pixels).
- Subpixel Anti-Aliasing
Render text for optimal horizontal placement.
- Hinting
Adjust font hinting, controls the spacing and crispness of text display.
- Interface Font
Replacement for the default user interface font.
- Mono-space Font
Replacement for the default mono-space interface font (used in the Text editor and Python Console).