Geometry Proximity Node¶
The Geometry Proximity node computes the closest location on the target geometry.
Tips
The Map Range Node is often helpful to use with the distance output of this node to create a falloff with a maximum distance.
Inputs¶
- Geometry
Standard geometry input.
- Group ID
Splits the elements of the input geometry into groups which can be sampled individually.
- Sample Position
The given position to calculate the closest location on the target.
- Sample Group ID
Determines in which group the closest nearest element is detected.
Properties¶
- Target Element
- Faces:
Calculate the closest point anywhere on the faces of the target’s mesh geometry.
- Edges:
Calculate the closest point anywhere on the edges of the target’s mesh geometry.
- Points:
Calculate the closest point or vertex on the target geometry. This mode is usually the fastest. This mode works for both point cloud and mesh geometry, the other modes only work for meshes.
Outputs¶
- Position
Closest location on the surface of the target mesh, or the closest point in the target point cloud in Points mode.
- Distance
Distance (as floating-point value) from the source position to the closest location in the target.
- Is Valid
Whether the sampling was successful. It can fail when the sampled group is empty.
Examples¶
The different modes of the node: faces, edges and points. In this example the Geometry Nodes modifier is added on the target plane. Note that the larger plane is subdivided and the smaller plane is not.
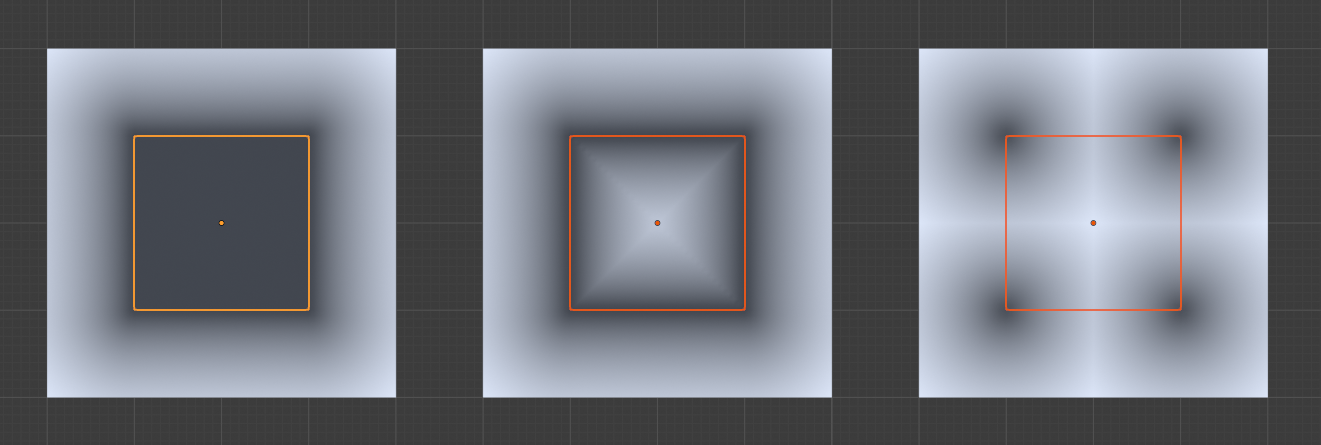
The three target element modes: faces, edges, and points.¶
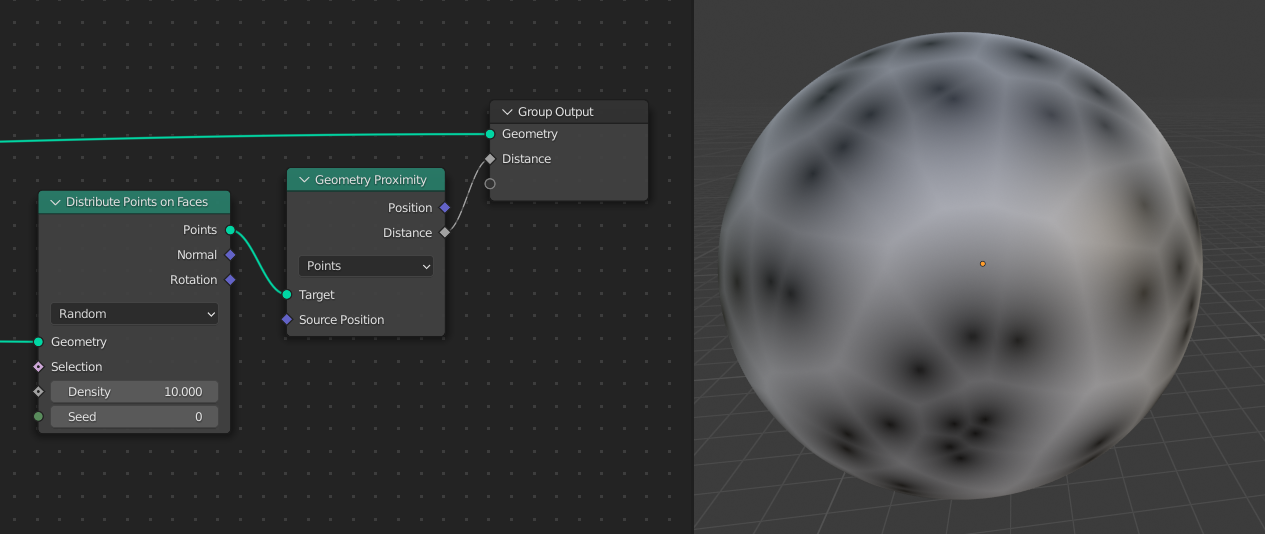
Points distributed on a sphere used as a target for a distance used in a shader.¶