Modifiers¶
Reference
- Panel:
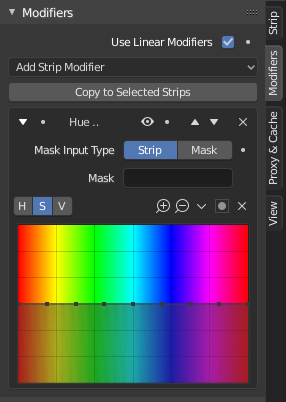
Modifiers are used to make adjustments to the image, like contrast, brightness, saturation, color balance and applying masks.
You can add these modifiers directly to a media strip, or you can use them within an Adjustment Layer strip, making them apply to several media strips in one go.
- Linear Modifiers
Calculates modifiers in linear color space instead of the Sequencer color space.
Calculating modifiers in linear space will match the image processing of the compositor. In most cases, this should be enabled; working in a non-linear workflow could have unpredictable results.
- Copy to Selected Strips
Copies the modifiers to the selected strips, either replacing their current modifiers or appending to them.
Common Options¶
Each modifier has several buttons at its top:
- Mute (eye icon)
Disables the modifier. Useful to compare the image with or without modifications.
- Move (up/down arrow icon)
These two buttons change the modifier's position in the stack which affects its computation order.
- (Remove Strip Modifier)
Deletes the modifier from the stack.
Masking¶
You can mask each modifier to limit the area of the image it affects. This can be done using either a Mask or another strip.
- Mask Input Type
Type of input data used for the mask.
- Strip:
Use the grayscale representation of another strip's image.
- Mask:
Use a Mask data-block.
- Mask
The Strip or Mask data-block to use.
- Mask Time Mask Input Only
How the start frame of the mask is calculated.
- Relative:
Mask animation is offset to the start of the strip.
- Absolute:
Mask animation is in sync with the scene frame.
Types¶
Currently, the following modifiers are supported:
Brightness/Contrast Modifier¶
Adjusts the brightness and contrast of the image.
Color Balance Modifier¶
Color balance adjustments, either by the Lift/Gamma/Gain or the Offset/Power/Slope method.
This modifier works similar to the Color Balance Node.
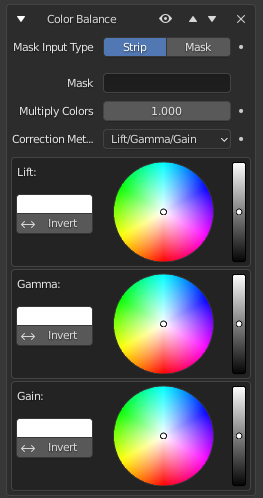
Depending on the selected method, the following operations can be applied to the color values in the sequencer color space:
- Lift/Gamma/Gain
- Lift
Increases the value of dark colors.
- Gamma
Adjusts midtones.
- Gain
Adjusts highlights.
- Offset/Power/Slope (ASC-CDL)
The following formula is applied to each RGB color value separately: \(c_{out} = (c_{in}×s + o)^p\)
- Slope
The multiplier \(s\) influences all color values except black. Its effect is stronger the brighter the source color is.
- Offset
Shifts color values after applying Slope by adding the Offset \(o\) to them. Note that the selected value shown in the UI will be reduced by 1, so the default value of 1 means effectively no offset is applied.
- Power
Overall exponent \(p\), which mainly adjusts the midtones.
Curves Modifier¶
Color and RGB curves.
This modifier works the same as the RGB Curves Node.
Hue Correct Modifier¶
HSV multi points curves.
This modifier works the same as the Hue Correct Node.
Mask Modifier¶
The mask modifier is used to affect the Alpha Channel of the current strip.
- Mask Input Type
Type of input data used for the mask.
- Strip:
Use the grayscale representation of another strip to affect the alpha of the current strip.
- Mask:
Use a mask data-block to affect the alpha of the current strip.
- Mask
The Strip or Mask data-block to use.
- Mask Time Mask Input Only
How the start frame of the mask is calculated.
- Relative:
Mask animation is offset to the start of the strip.
- Absolute:
Mask animation is in sync with the scene frame.
Tone Map Modifier¶
Used to map one set of colors to another in order to approximate the appearance of high dynamic range images in a medium that has a more limited dynamic range.
This modifier works the same as the Tone Map Node.
White Balance Modifier¶
Used to adjust the white balance by choosing the color that should be white.
Sound Equalizer Modifier¶
This modifier can be used to emphasize or suppress sound frequencies. The range is limited to 35Hz - 20kHz and +/-35dB.