Compare Node¶
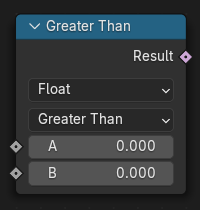
The Compare node takes two inputs and does an operation to determine whether they are similar. The node can work on all generic data types, and has modes for vectors that contain more complex comparisons, which can help to reduce the number of necessary nodes, and make a node tree more readable.
Inputs¶
- A, B
Standard value inputs of the selected type.
- C
Compared against the dot product of two input vectors in when the Mode property is set to Dot Product.
- Epsilon
This value is used as a threshold for still considering the two inputs as equal for the Equal and Not Equal operations.
Properties¶
- Mode
- Element-Wise:
Compare each axis of the input vectors separately, and output true only when the result is true for each axis.
- Length:
Compare the length of the two input vectors.
- Average:
Compare the average of the elements of the input vectors. This is the same as the implicit conversion used when setting the node's data type to Float.
- Dot Product:
Compare the dot product of the two vectors with the separate C input, using the selected operation. The dot product outputs a single value that says how much the two vectors "agree".
- Direction:
Compare the angle between the two vectors with the separate Angle input, using the selected operation. The vectors are normalized, so their length does not matter.
- Operation
- Less Than:
True when the first input is smaller than second input.
- Less Than or Equal:
True when the first input is smaller than the second input or equal.
- Greater Than:
True when the first input is greater than the second input.
- Greater Than or Equal:
True when the first input is greater than the second input or equal.
- Equal:
True when both the difference between the two inputs is smaller than the Epsilon input.
- Not Equal:
True when both the difference between the two inputs is larger than the Epsilon input.
- Brighter:
True when the first color input is brighter than the second.
- Darker:
True when the first color input is darker than the second.
Output¶
- Result
Standard Boolean output.
Examples¶
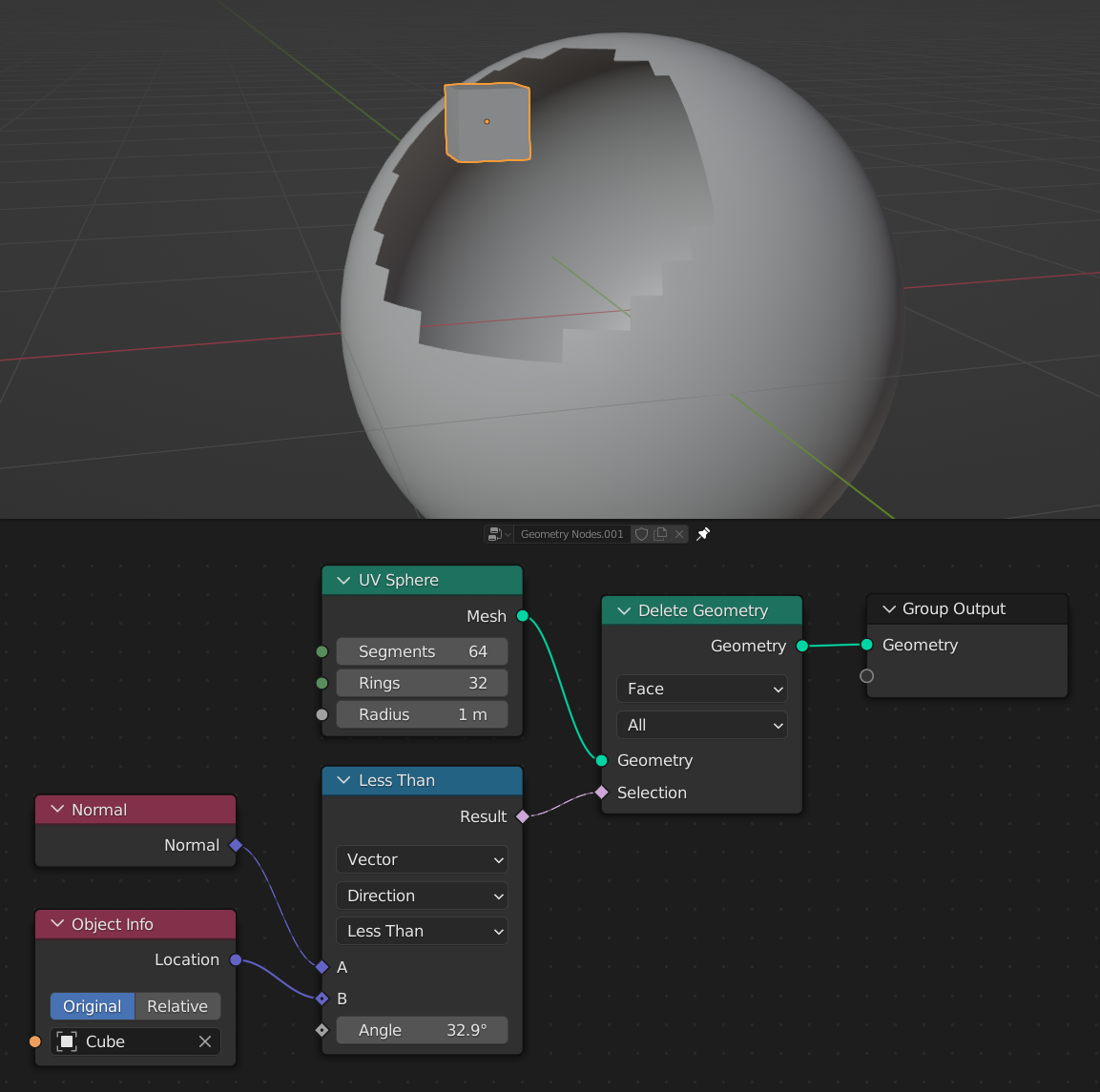
Here, the compare node is used with the Direction mode to compare the direction of the sphere's face normals to the "direction" of the cube object's location. Anywhere that the directions are less than 32.9 degrees apart, the faces will be selected, and deleted.