Camera¶
This panel contains all settings of the camera used for filming the movie which is currently being edited in the Clip editor. Different predefined settings can be used here and can be chosen from the panel header. But such settings as distortion coefficients and principal point are not included in the presets and should be filled in even if camera presets are used.
- Sensor Width
Is the width of the CCD sensor in the camera. This value can be found in camera specifications.
- Pixel Aspect
Is the pixel aspect of the CCD sensor. This value can be found in camera specifications, but can also be guessed. For example, you know that the footage should be 1920×1080, but the images themselves are 1280×1080. In this case, the pixel aspect is: 1920 / 1280 = 1.5.
Lens¶
- Focal Length
Is self-explanatory; it is the focal length with which the movie was shot. It can be set in millimeters or pixels.
- Optical Center
Is the optical center of the lens used in the camera. In most cases it is equal to the image center, but it can be different in some special cases. Check camera/lens specifications in such cases.
Tip
Optical Center also know as the principal point in photogrammetry.
- Set Center
- Lens Distortion
Mathematical function to convert distorted to undistorted coordinates.
- Polynomial:
Polynomial radial distortion. Uses three distortion coefficients: K1, K2, and K3.
- Division:
It defines high distortions, which makes this model suitable much better for cameras with fisheye lenses. Use two distortion coefficients: K1, K2.
- Nuke:
Distortion model used by the Nuke compositor. Use two distortion coefficients K1, K2.
- Brown:
Brown-Conrady is one of most advanced mathematical lens distortion models. Used to model both radial and tangential distortion. Can use up to four radial distortion coefficients: K1 - K4 and up to two tangential distortion coefficients: P1 and P2.
- Coefficients
Coefficients are used to compensate for lens distortion when the movie was shot. Currently these values can be tweaked by hand only (there are no calibration tools yet) using tools available in Distortion mode. To do this tweak K1 until the solving is the closest to the known focal length (but also take grid and annotations into account to prevent “impossible” distortion).
- Radial Distortion Coefficients (K1 - K4)
The coefficients in lens distortion models work independent from each other. Positive values will give a barrel distortion while negative values give a pincushion distortion. With a mixture of both negative and positive coefficients you can define more complicated mustache distortions or other complex distortions, that are less common but not rare.
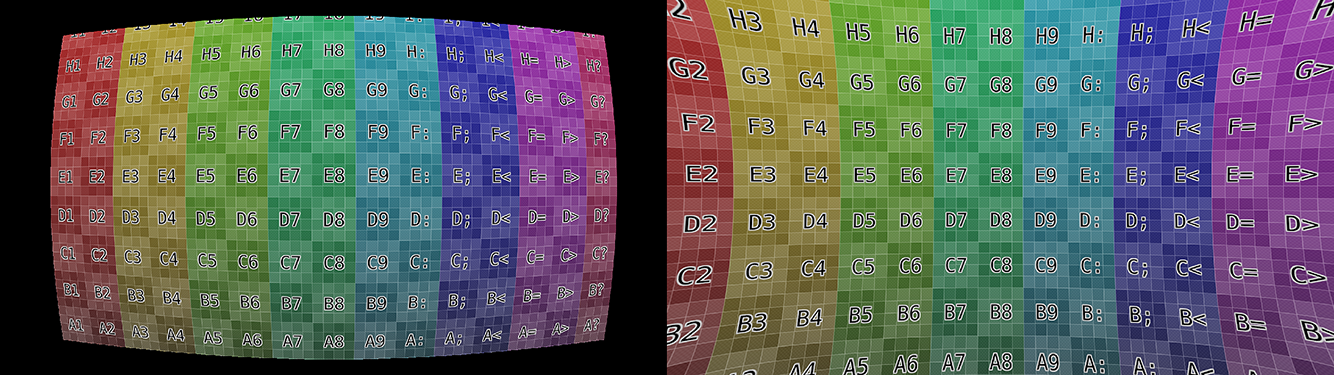
Example of radial distortion for positive and negative K coefficients.¶
- Tangential Distortion Coefficients (P1, P2)
Works independent and allow to compensate for situations when the sensor is not perpendicular to a group of lens. The optical center (also called principal point) will be shifted (distorted) from the center of the sensor. P1 is used to compensate for sensor rotation in Z (vertical) axes, while P2 is for compensating sensor rotation in X (horizontal) axes. Such distortions can be found in sources from cameras with a sensor stabilization system.
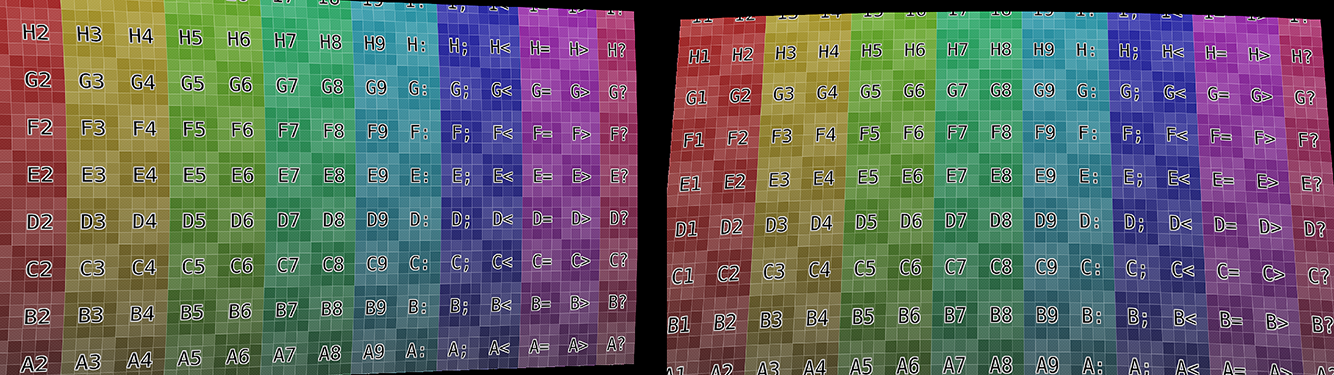
Example of tangential distortion for P coefficients.¶