Areas¶
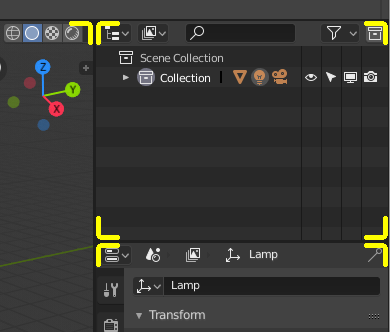
Area boundaries are indicated by rounded corners (yellow highlights).¶
The Blender window is divided into a number of rectangles called Areas. Areas reserve screen space for 편집기(editor), such as the 3D Viewport or the Outliner. Each editor offers a specific piece of functionality.
Areas are grouped into Workspaces, which are geared towards particular tasks (modeling, animating and so on).
참고
While some keyboard shortcuts in Blender are global (such as Ctrl-S for saving), many depend on which editor the mouse cursor is hovering over.
As an example, say you just selected two objects in the Outliner and want to join them. If you pressed the shortcut for this (Ctrl-J) while the cursor is still in the Outliner, nothing would happen as the shortcut isn’t valid there; you first need to move your cursor to the 3D Viewport.
Resizing¶
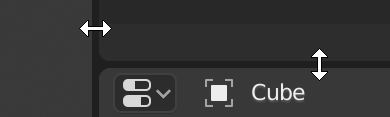
You can resize areas by dragging their borders with LMB. Move your mouse cursor over the border between two areas, so that the cursor changes to a double-headed arrow, and then click and drag.
팁
Hold Ctrl to snap the size of areas to convenient sizes.
Docking¶
Docking describes several ways an area a user can interactively manipulate the size and location of areas along with splitting an area into new areas.
To start the interactive process, placing the mouse cursor in an area corner will change the cursor to a cross (+). Once the cursor is a cross, press and hold LMB to preform any of the following actions:
If you press Esc or RMB before releasing the mouse, the operation will be canceled.
Joining¶
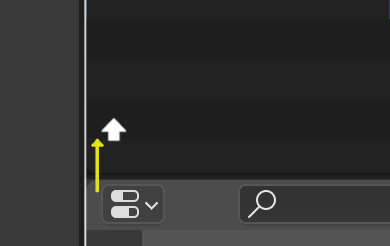
Properties is being joined to the Outliner.¶
Dragging from an area corner into the space of a second area will join two areas. The areas that will be joined will be displayed brighter.
Splitting¶
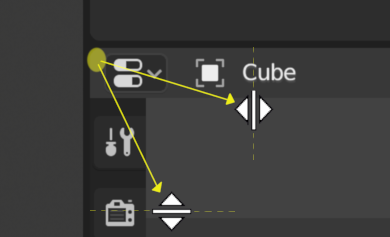
Splitting an area will create a new area. Dragging from an area corner left/right will split the area vertically, to split the area horizontally drag up/down.
You can split and join areas at once by dragging a split operation into a separate area.
Dragging an area into the middle of an second area will replace the second area with the first area.
Area Options¶
RMB on the border opens the Area Options.
- Vertical/Horizontal Split
Shows an indicator line that lets you select the area and position where to split. Tab switches between vertical/horizontal.
- Join Up/Down/Left/Right
Shows the join direction overlay.
- Swap Areas
Swaps this area with the adjacent one.
Swapping Contents¶
You can swap the contents of two areas by pressing Ctrl-LMB on one of the corners of the initial area, dragging towards the target area, and releasing the mouse there. The two areas do not need to be side-by-side, though they must be inside the same window.
Duplicate Area into new Window¶
Reference
- Menu:
A new floating window containing an area can be created from . (Not available in some editors.)
The new window is a fully functional window, which is part of the same instance of Blender. This can be useful, e.g. if you have multiple monitors.
You can also create a new window from an existing area by pressing Shift-LMB on an area corner, then dragging outward slightly.
Toggle Maximize Area¶
Reference
- Menu:
- 단축키(hotkey):
Ctrl-Spacebar
Expands the Area so it fills the whole window (while keeping the Topbar and Status Bar visible). To return to normal size, use the keyboard shortcut again or click the Back to Previous button in the Topbar.
Toggle Fullscreen Area¶
Reference
- Menu:
- 단축키(hotkey):
Ctrl-Alt-Spacebar
Expands the Area so it fills the whole window, hiding the Topbar, Status Bar, and even the secondary regions (toolbars etc.) of the Area’s own editor. To return to normal size, use the keyboard shortcut again or click the icon in the Area’s top right corner (only becomes visible when hovering).