Numeric Input¶
Using the mouse for transformations is convenient, but if you require more precise control, you can also enter numeric values. After pressing the shortcut type a number to indicate the magnitude of the transformation. Then confirm or cancel. E.g. pressing S 2, Return will double the scale of an object.
- Move G
By default and with no other key presses, the translation will occur along the X axis.
- Rotation R
The rotation is in clockwise direction for positive values.
- Scale S
Scaling works in almost identical fashion to translation. The primary difference is that by default, scaling applies equally to all three axes.
You can see the numbers you enter in the 3D Viewport footer.
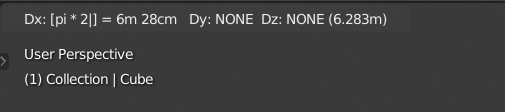
Numeric input displayed in the footer.¶
팁
Numeric input can also be inputted in the Properties region.
Simple Mode¶
Blender has two “modes” a simple and an advanced one. Simple mode only accepts simple numbers. You can use basic text editing except selection.
- Decimals Period
Decimals can be entered by pressing Period.
- Negate Minus
Negate the whole value by pressing Minus.
- Inverse Slash
Hitting Slash during number entry switches the number being entered to its reciprocal, e.g.
2 /results in 0.5 (1/2);20 /results in 0.05 (1/20).- Reset Backspace
Hitting Backspace after having deleted all leading chars will first reset the edited value to initial state, and on second press, the whole number editing will be canceled, going back to usual transform with mouse.
- Next/Previous Component Tab, Ctrl-Tab
To enter numeric values for multiple axes, use Tab or Ctrl-Tab. E.g. To move an object, one unit on all three axes press: G 1 and Tab 1 and Tab 1.
- Non-number Inputs
You can also combine numeric input with Axis Locking to limit movement to a particular axis or tool specific shortcuts.
Advanced Mode¶
In advanced mode you can additionally enter expressions and units.
Use = or NumpadAsterisk to enable advanced mode, and Ctrl-= or Ctrl-NumpadAsterisk to switch back to simple mode.
It features:
Units (
cm,",deg, etc.). See unit system.Basic operations from Python (
+,*,/,**, etc.).Math constants and functions (
pi,sin,sqrt, etc.). See Python’s math module.
You can still use the negate and inverse shortcuts (Minus, Slash), as well as non-number inputs, but you have to hold Ctrl to activate them.