Light Settings¶
Reference
- 패널:
and
Next to lighting from the background and any object with an emission shader, lights are another way to add light into the scene. The difference is that they are not directly visible in the rendered image, and can be more easily managed as objects of their own type.
Common¶
Light settings for all renderers.
Cycles¶
- Max Bounces
Maximum number of times light from the light is allowed to Bounce. Limited by scene-wide bounce settings.
- Cast Shadow
By disabling this option, light from lights will not be blocked by objects in between. This can speed up rendering by not having to trace rays to the light source.
- Multiple Importance Sample
By default lights use only direct light sampling. For area lights and sharp glossy reflections, however, this can be noisy, and enabling this option will enable indirect light sampling to be used in addition to reduce noise.
- Shadow Caustics
Mark a light as a refractive caustic caster. This setting can be used in conjunction with the Cast and Receive caustics object settings to selectively speed up refractive caustic rendering of select objects.
Area Lights¶
- Portals
Area lights can also function as light portals to help sample the environment light, and significantly reduce noise in interior scenes. Note that rendering with portals is usually slower, but as it converges more quickly, less samples are required.
Light portals work by enabling the Portal option, and placing areas lights in windows, door openings, and any place where light will enter the interior.
In outdoor scenes most rays do not bounce much and just fly off into the sky and therefore, light portals are not helpful for outdoor scenes.


White Room model by Jay Hardy.¶
Beam Shape¶
- Spread
How wide the emitted light fans out controlling how diffused the light is. Larger values create soft shadows while smaller values create sharper light simulating a gridded softbox.
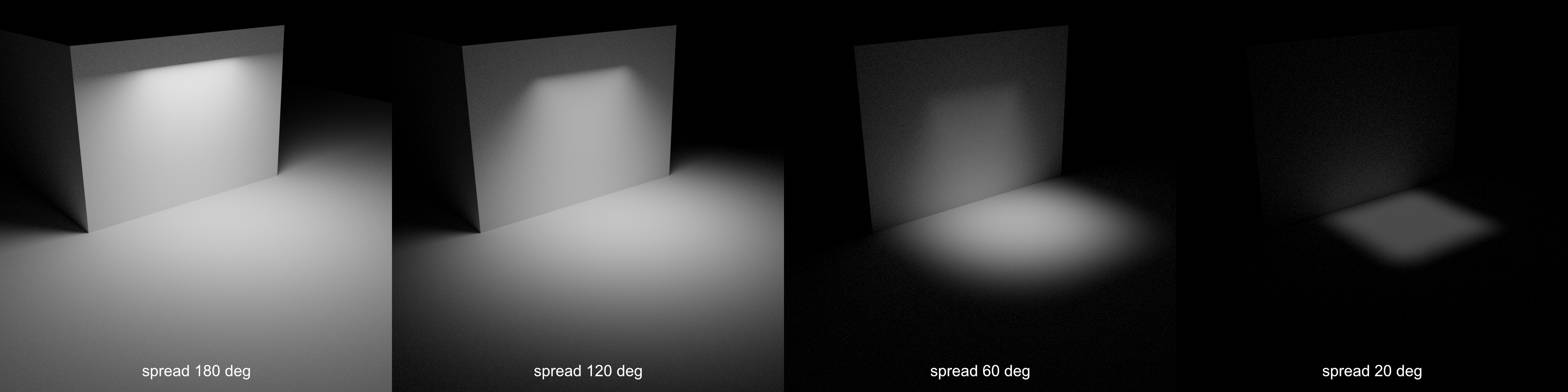
Example of Spread at different angles.¶