原理化 BSDF#
The Principled BSDF that combines multiple layers into a single easy to use node. It can model a wide variety of materials.
It is based on the OpenPBR Surface shading model, and provides parameters compatible with similar PBR shaders found in other software, such as the Disney and Standard Surface models. Image textures painted or baked from software like Substance Painter may be directly linked to the corresponding input in this shader.
层#
The base layer is a mix between metal, diffuse, subsurface, and transmission components. Most materials will use one of these components, though it is possible to smoothly mix between them.
The metal component is opaque and only reflect lights. Diffuse is fully opaque, while subsurface also involves light scattering just below the surface. Both diffuse and subsurface sit below a specular layer. The transmission component includes both specular reflection and refraction.
On top of all base layers there is an optional glossy coat. And finally the sheen layer sits on top of all other layers, to add fuzz or dust.
Light emission can also be added. Light emits from below the coat and sheen layers, to model for example emissive displays with a coat or dust.
输入#
- 基础色
Overall color of the material used for diffuse, subsurface, metal and transmission.

相同基础色用于不同材质类型#
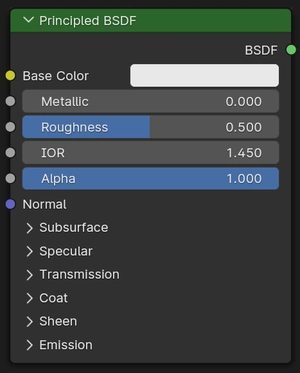
- 粗糙度
Specifies microfacet roughness of the surface for specular reflection and transmission. A value of 0.0 gives a perfectly sharp reflection, while 1.0 gives a diffuse reflection.

粗糙度位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- 金属度
绝缘体和金属材料模型之间混合,0.0时,材质由漫反射或透射基础层组成,顶部有高光反射层。值为1.0时,会产生完全镜面反射,并使用基本颜色着色,而不会产生漫反射或透射。

金属度位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- IOR
Index of refraction (IOR) for specular reflection and transmission. For most materials, the IOR is between 1.0 (vacuum and air) and 4.0 (germanium). The default value of 1.5 is a good approximation for glass.

IOR 位于 1.0 至 2.0 之间#
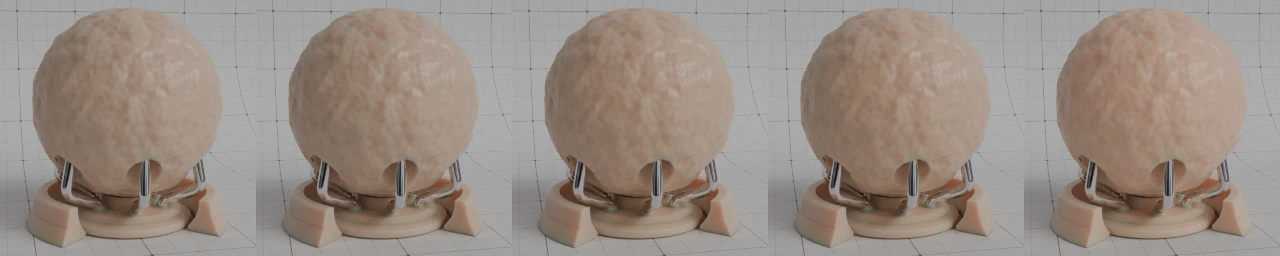
- Alpha
控制表面的透明度,数值设定为1.0时,表面完全不透明。通常连接到 "图像纹理" 着色器节点的Alpha输出接口。
Alpha 位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- 法向
控制基础图层的法线方向。
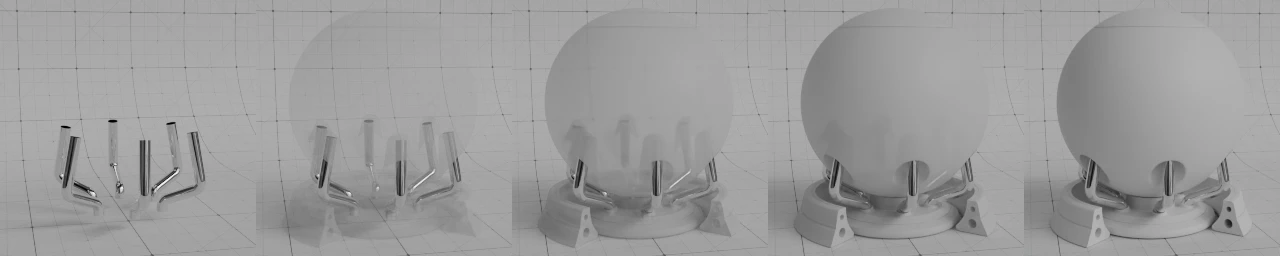
次表面#
Subsurface scattering is used to render materials such as skin, milk and wax. Light scatters below the surface to create a soft appearance.
- 方法
Rendering method to simulate Subsurface scattering.
- 克里斯坦森-伯利:
基于物理的体积散射的近似值。此方法不如 随机游走 准确,但是,在某些情况下,此方法将更快地解决噪声。
- 随机游走:
Cycles Only Provides accurate results for thin and curved objects. Random Walk uses true volumetric scattering inside the mesh, which means that it works best for closed meshes. Overlapping faces and holes in the mesh can cause problems.
- 随机游走(皮肤):
Cycles Only Random walk method optimized for skin rendering. The radius is automatically adjusted based on the color texture, and the subsurface entry direction uses a mix of diffuse and specular transmission with custom IOR. This tends to retain greater surface detail and color and matches measured skin more closely.
- 权重
漫反射表面和次表面散射之间的混合。通常应为0或1(完全漫反射或次表面)。

权重位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- 半径
光散射到表面下方的平均距离。较高的半径可以使外观更柔和,因为光线会流入阴影区域并穿过物体。散射距离是针对RGB通道单独指定的,对于具有较强红光散射的面板材质,渲染效果较佳。X,Y和Z的数值会分别映射到R,G和B的值。

半径位于白色到红色之间#
- 比例|缩放
应用于半径的缩放值。

缩放位于 0 cm 至 50 cm 之间#
- IOR 仅限 Cycles
Index of refraction (IOR) used for rays that enter the subsurface component. This may be set to a different value than the global IOR to simulate different layers of skin.

IOR 位于 1.0 至 2.0 之间#
- 各向异性 仅限 Cycles
次表面中体积散射的方向性。零为所有方向上均匀散射,值越高,向前散射越强烈。例如,皮肤已被测定为具有0.8的各向异性。
各向异性位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
镜面反射#
Controls for both the metallic component and specular layer on top of diffuse and subsurface.
- 分布
要使用的微面分布。
- GGX:
A method that is faster than Multiple-scattering GGX but is less physically accurate.
- 多重散射GGX:
Takes multiple scattering events between microfacets into account. This gives more energy conserving results, which would otherwise be visible as excessive darkening.
- 折射率等级
Adjustment to the IOR to increase or decrease intensity of the specular layer. 0.5 means no adjustment, 0 removes all reflections, 1 doubles them at normal incidence.
This input is designed for conveniently texturing the IOR and amount of specular reflection.

IOR 等级位于 0.0 到 1.0 之间#
- 染色
Color tint for specular and metallic reflection.
For non-metallic tints provides artistic control over the color specular reflections at normal incidence, while grazing reflections remain white. In reality non-metallic specular reflection is fully white.
For metallic materials tints the edges to simulate complex IOR as found in materials such as gold or copper.

染色位于白色到黄色之间#
- 各向异性 仅限 Cycles
镜面反射的各向异性量。较高的设定值可提供沿切线方向的细长高光;设定为负值则会给出垂直于切线方向的高光。

各向异性过滤位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- 各向异性旋转 仅限 Cycles
旋转各向异性的方向,取值为1.0时,旋转一周。
与 各向异性 BSDF 着色器节点不同,该节点的高光延伸方向会旋转90°。可通过增加0.25的旋转值进行更正。

各向异性旋转位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- 切向 (正切)
控制各向异性的切向。
透射#
Transmission is used to render materials like glass and liquids, where the surface both reflects light and transmits it into the interior of the object
- 权重
Mix between fully opaque surface at zero and fully transmissive at one.
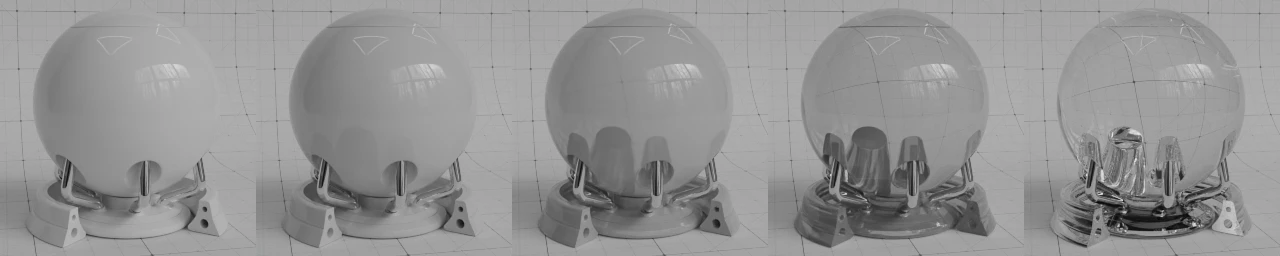
权重位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
涂层#
Coat on top of the materials, to simulate for example a clearcoat, lacquer or car paint.
- 权重
Controls the intensity of the coat layer, both the reflection and the tinting. Typically should be zero or one for physically-based materials, but may be textured to vary the amount of coating across the surface.

权重位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- 粗糙度
涂层的粗糙度。

粗糙度位于 0.0 至 1.0 之间#
- IOR
Index of refraction (IOR) of the coat layer. Affects its reflectivity as well as the falloff of coat tinting.

IOR 位于 1.0 至 2.0 之间#
- 染色
通过创建一个吸收层,给涂层添加一个带颜色的染色。随着光在介质中传播得更远(取决于涂层IOR),在较浅的角度饱和度增加。

染色位于白色到蓝色之间#
- 法向
Controls the normals of the Coat layer, for example to add a smooth coating on a rough surface.
光泽#
Sheen simulates very small fibers on the surface. For cloth this adds a soft velvet like reflection near edges. It can also be used to simulate dust on arbitrary materials.
自发光(发射)#
来自表面的自发光。
薄膜 仅限 Cycles#
Thin Film simulates the effect of interference in a thin film sitting on top of the material. This causes the specular reflection to be colored in a way which strongly depends on the view angle as well as the film thickness and the index of refraction (IOR) of the film and the material itself.
This effect is commonly seen on e.g. oil films, soap bubbles or glass coatings. While its influence is more obvious in specular highlights, it also affects transmission.
Note
Thin-film interference is currently only applied to dielectric materials. Support for thin films on top of Metallic is planned in the future.
- 厚(宽)度
The thickness of the film in nanometers. A value of 0 disables the simulation. The interference effect is strongest between roughly 100 and 1000 nanometers, since this is near the wavelengths of visible light.
- IOR
Index of refraction (IOR) of the thin film. The common range for this value is between 1.0 (vacuum and air) and roughly 2.0, though some materials can reach higher values. The default value of 1.33 is a good approximation for water. Note that when the value is set to 1.0 or to the main IOR of the material, the thin film effect disappears since the film optically blends into the air or the material.
输出#
- BSDF
标准着色器输出。




