Curva guia¶
Reference
- Panel:
- Tipo:
Curva guia
The Curve Guide is used to force particles to follow a certain path defined by a Curve Object. A typical scenario would be to move a red blood cell inside a vein, or to animate the particle flow in a motor. You can also use Curve Guide to shape certain hair strands.
Nota
You can also use the Particle Edit Mode to define a path.
Since you can animate curves as a soft body or any other usual way, you may build very complex animations while keeping great control and keeping the simulation time to a minimum.
To make particles point in the direction of the curve, you need to set their Orientation Axis to Velocity / Hair, enable Dynamic, and set their Angular Velocity Axis to Velocity, all in the the Rotação settings of the particle system. The Follow Path Constraint and the curve’s legacy Follow option won’t work for this.
A Curve Guide force affects all particles on the same layer, independently from their distance to the curve. If you have several guides in a layer, their fields add up to each other (the way you may have learned it in your physics course). But you can limit their influence radius by changing the Minimum Distance (see below).
A particle follows a Curve Guide during its lifetime, the velocity depends on its lifetime and the length of the path.
Nota
The Curve Guide does not affect soft bodies.
Opções¶
- Livre
Fraction of particle life time, that is not used for the curve.
- Falloff Power
This setting governs the strength of the guide between Min Distance and Max Distance. A falloff of 1 means a linear progression.
- Aditivo
If you use Additive, the speed of the particles is also evaluated depending on the falloff.
- Pesos de influência
Permite usar curvas de peso para influenciar a influência das partículas ao longo da curva.
- Quantidade de aglomeração
The particles come together at the end of the curve (1) or they drift apart (-1).
- Shape
Defines the form in which the particles come together. +0.99: the particles meet at the end of the curve. 0: linear progression along the curve. -0.99: the particles meet at the beginning of the curve.
- Distância mínima
The distance from the curve, up to where the force field is effective with full strength. If you have a falloff of 0, this parameter will have no effect, because the field is effective with full strength up to Max Distance (or the infinity). Min Distance is shown with a circle at the endpoints of the curve in the 3D Viewport.
- Distância máxima
The maximum influence radius. Shown by an additional circle around the curve object.
Kink¶
Aviso
This feature is broken in the current version, see Bug Report #46776.
- Tipo
Changes the shape that the particles can take.
- None:
A ser feito.
- Trançar:
Trançado.
- Encaracolar:
The radius of the influence depends on the distance of the curve to the emitter.
- Radial:
A three-dimensional, standing wave.
- Roll:
A one-dimensional, standing wave.
- Rotação:
A ser feito.
- Ondas:
A two-dimensional, standing wave.
It is not so easy to describe the resulting shapes, so have a look at the example below.

Kink options of a curve guide. From left to right: Radial, Wave, Braid, Roll. Animation.¶
- Eixos
Which axis to use for the offset.
- Frequência
A frequência do deslocamento.
- Shape
Ajusta o deslocamento para o início ou para o final.
- Amplitude
A amplitude do deslocamento.
Examples¶
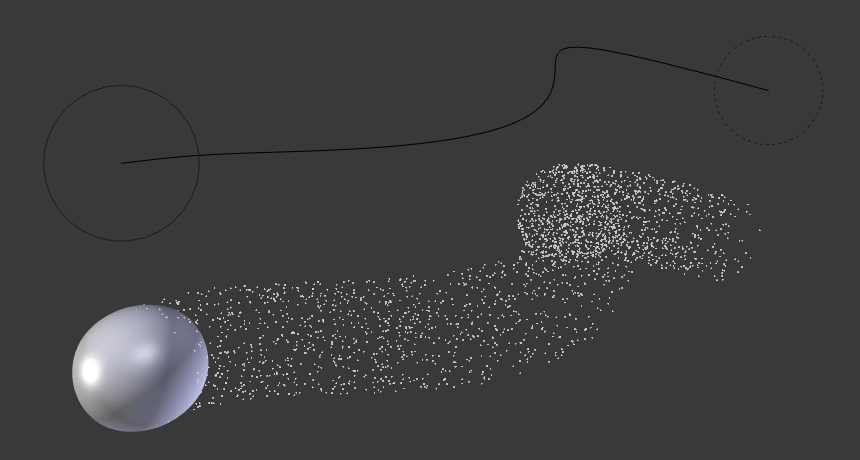
O campo de força do tipo Curva guia.¶