Cobertura¶
The Skin modifier uses vertices and edges to create a skinned surface, using a per-vertex radius to better define the shape. The output is mostly quads, although some triangles will appear around intersections.
É uma forma rápida para gerar malhas de base para esculpir e/ou forma orgânicas suaves com topologia arbitrária.
Nota
Faces in the original geometry are ignored.
Opções¶
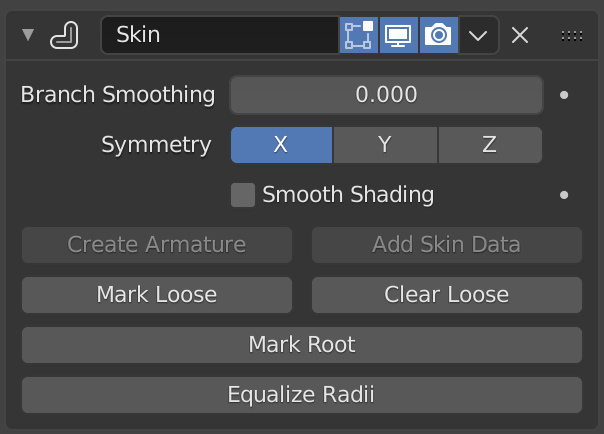
The Skin modifier.¶
- Suavização das ramificações
A branch point is a vertex with three or more connected edges. These areas tend to produce more complicated topology, some of which may overlap. This setting relaxes the surface around these points, with the side effect of shrinking it.
- Symmetry
These checkboxes are used to keep the output topology symmetrical in their respective axes. In other words, using it avoids merging triangles across an axis unless the triangles form a symmetric quad.
Nota
They do not add geometry flipped across an axis. For that, the Mirror modifier should be used, typically placed above the Skin one.
- Smooth Shading
Resulta em faces com suavização de sombreamento ao invés de sombreamento achatado. O sombreamento suave/achatado da geometria de entrada não é preservado.
- Criar Armação
Cria uma armadura em cima do objeto. Cada aresta torna-se um osso.
Nota
Se o vértice raiz possui mais que uma aresta adjacente, um osso adicional será criado para servir de raiz.
Esta ferramenta faz o seguinte:
Um novo objeto armadura é adicionado com ossos correspondendo a malha de entrada. A seleção ativa é trocada para a nova armadura.
Weight groups are added to the input mesh. The Skin modifier propagates these weights to the output as well.
An Armature modifier is added directly below the Skin one. Note that the Armature modifier is being applied after the Skin one because it should only deform the output, whereas if it were above, it might change the resulting topology.
- Add Skin Data
This modifier uses a custom set of data in the mesh, that is generated automatically when you add the modifier the first time.
However, you may remove that data, or loose it some way or the other. That operator will generate it again.
- Marcar ou limpar os soltos
By default, a branch vertex (vertex with three or more connected edges) will generate extra edge loops along adjacent edges in order to keep the output tight. Branches can be made loose by clicking Mark Loose, which will allow the output to stretch between all adjacent vertices. This can be disabled again by clicking Clear Loose.
- Marcar como raízes
Marking a vertex as root causes that vertex to be used for calculating rotations for connected limbs. Root vertices also affect the armature output, they will be used as the origin for the root bones.
Each set of connected vertices should have one root node (one is selected by default if you do not assign any manually). Mark Root enforces the one-root per set rule, so it is not necessary to manually unmark roots.
- Equalizar raios
Torna os raios da cobertura dos vértices selecionados iguais em cada eixo.
Skin Mesh Data¶
That modifier needs a set of specific data in the original mesh to work properly. This data allows you to define the root vertices of each tree, which ones are loose, and the size (radius) of the skin at each vertex. The radii of input vertices can be individually scaled in Edit Mode with the Skin Resize.
Examples¶
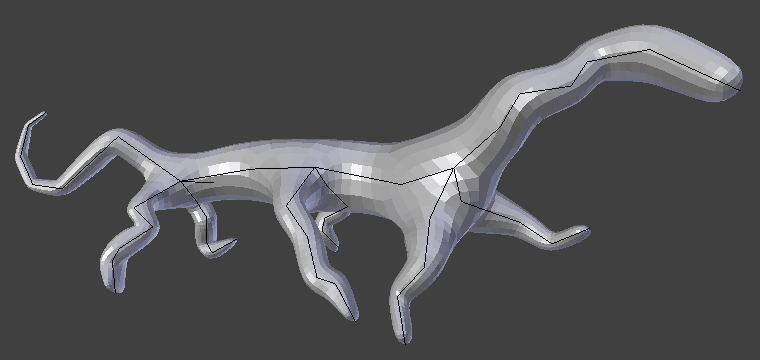
Simple creature, made with only the Skin and Subdivision Surface modifiers.¶
Ligações externas¶
Skin Modifier Development at Blender Nation – An early demonstration of the Skin Modifier by Nicholas Bishop (March 2011).
Ji, Zhongping; Liu, Ligang; Wang, Yigang (2010). B-Mesh: A Fast Modeling System for Base Meshes of 3D Articulated Shapes, Computer Graphics Forum 29(7), pp. 2169-2178. – The work this modifier is based on (DOI 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2010.01805.x).