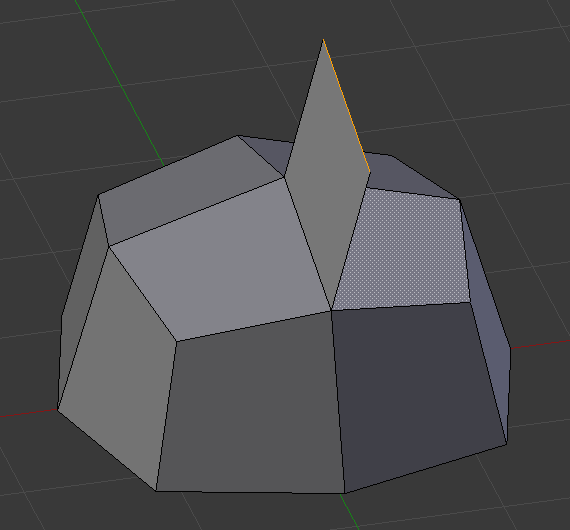
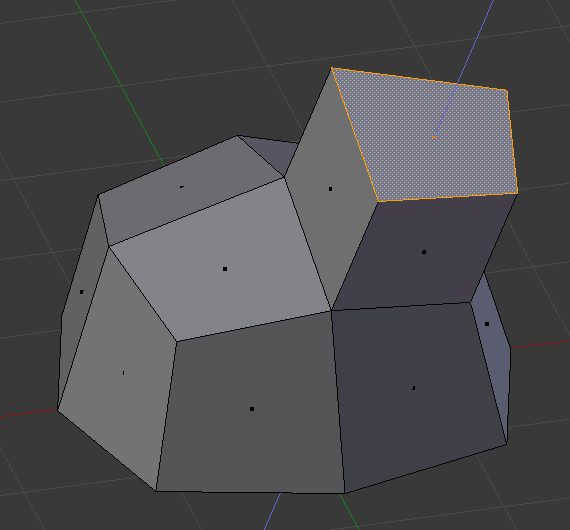
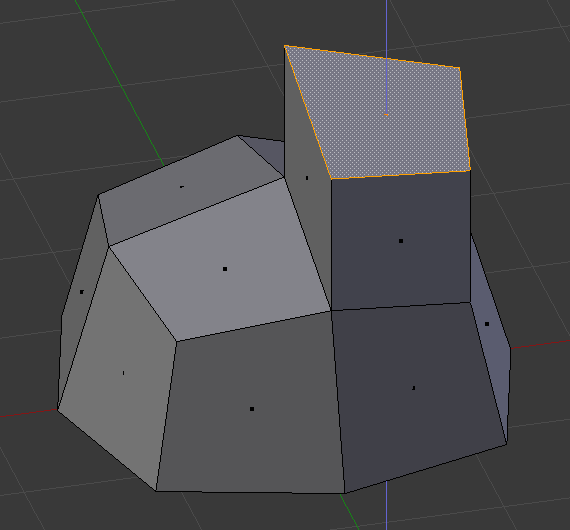
Đẩy Trồi Vùng (Extrude Region)¶
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Chế Độ (Mode):
Chế Độ Biên Soạn (Edit Mode)
- Công Cụ (Tool):
- Tổ Hợp Phím Tắt (Shortcut):
E
Extrusion tools duplicate vertices, while keeping the new geometry connected with the original vertices. Vertices are turned into edges and edges will form faces.
Công cụ này có tầm quan trọng hàng đầu đối với việc kiến tạo các hình học mới. Nó cho phép bạn kiến tạo các hình bình hành từ hình chữ nhật và hình trụ từ các hình tròn, đồng thời dễ dàng kiến tạo những thứ như các chi nhánh của cây cối.
The axis on which vertices and edges are extruded along can be set interactively. Faces are extruded by default along their averaged normal. The extrusion can be limited to a single axis by specifying an axis; see Khóa Trục (Axis Locking).
The extrude tools differentiate in how the new geometry is connected in itself.
Only the border loop gets extruded. The inner region of the selection gets moved unchanged with the extrusion.
Chi Tiết (Details)¶
Although the process is quite intuitive, the principles behind Extrude are fairly elaborate as discussed below:
First, the algorithm determines the outside edge loop of the extrude; that is, which among the selected edges will be changed into faces. By default (see below), the algorithm considers edges belonging to two or more selected faces as internal, and hence not part of the loop.
The edges in the edge loop are then changed into faces.
If the edges in the edge loop belong to only one face in the complete mesh, then all of the selected faces are duplicated and linked to the newly created faces. For example, rectangles will result in parallelepipeds during this stage.
In other cases, the selected faces are linked to the newly created faces but not duplicated. This prevents undesired faces from being retained "inside" the resulting mesh. This distinction is extremely important since it ensures the construction of consistently coherent, closed volumes at all times when using Extrude.
When extruding completely closed volumes (like e.g. a cube with all its six faces), extrusion results merely in a duplication, as the volume is duplicated, without any link to the original one.
Edges not belonging to selected faces, which form an "open" edge loop, are duplicated and a new face is created between the new edge and the original one.
Single selected vertices which do not belong to selected edges are duplicated and a new edge is created between the two.