Nút Chất Liệu Hình Ảnh (Image Texture Node)¶
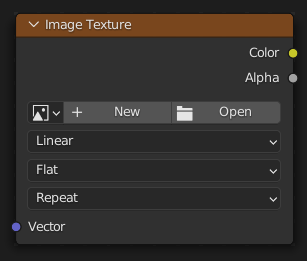
Used for applying an image as a texture.
Đầu Vào (Inputs)¶
- Véctơ (Vector)
3D coordinate that's projected onto the 2D image using the selected Projection method. The node then outputs the color and alpha at this projected point.
This slot is usually connected to an output of the Nút Tọa Độ Chất Liệu (Texture Coordinate Node). If left unconnected, the coordinate is taken from the object's active UV map (with Z = 0).
Tính Chất (Properties)¶
- Hình Ảnh (Image)
Image data-block to use.
- Interpolation (Nội Suy)
Method to scale images up or down for rendering.
- Tuyến Tính (Linear):
Nội suy chất lượng thông thường.
- Lập Phương/Bậc Ba (Cubic):
Smoother, better quality interpolation. Bump maps should use this for best results.
- Gần Nhất (Closest):
No interpolation (nearest neighbor). Useful for rendering pixel art.
- Thông Minh (Smart):
Cycles Only Only for Open Shading Language. Use cubic interpolation when scaling up and linear when scaling down, for better performance and sharpness.
- Projection (Phóng Chiếu)
How to project Vector onto the image for arriving at a color.
- Phẳng Bẹt (Flat):
Place the image in a unit square (stretching from (0, 0, 0) to (1, 1, 0)) and project the Vector vertically onto it. This projection is typically used in combination with UV maps.
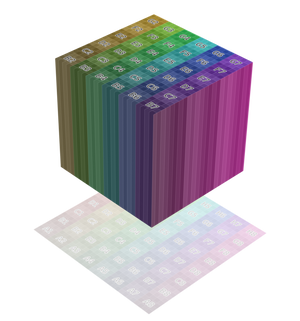
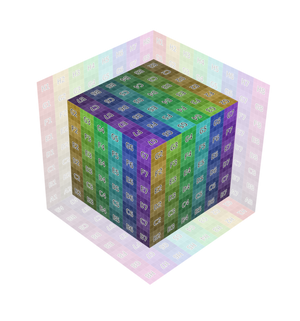
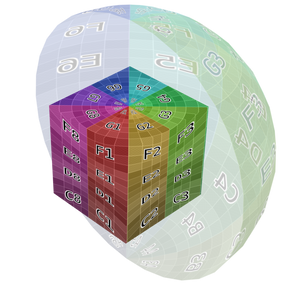
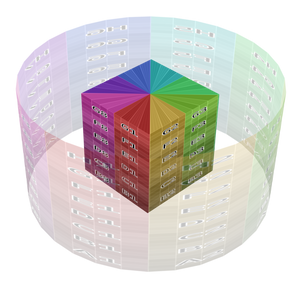
- Hình Hộp (Box):
Place the image on each side of a unit cube (stretching from (0, 0, 0) to (1, 1, 1)) and project the Vector onto this cube, along the axis that's closest to the mesh normal. This projection is commonly used in architectural models considering these have lots of box-shaped objects.
- Pha Trộn (Blend)
Rather than projecting onto just one side (which creates sharp transitions), project onto multiple sides and blend the results together. The higher the value, the more blending and the smoother the result.
- Hình Cầu (Sphere):
Wrap the image around a sphere with origin (0.5, 0.5, 0.5), and project the Vector from this origin onto this sphere. This projection is, of course, perfect for spherical objects such as planets, and is also useful for organic objects.
- Hình Ống (Tube):
Wrap the image around a cylinder with base (0.5, 0.5, 0) and height 1, and project the Vector horizontally from the central axis onto this cylinder. This projection is useful for a label on a bottle, for example. However, it's not suited for the top or bottom side of objects.
- Mở Rộng (Extension)
How the image is extrapolated if Vector lies outside the regular (0, 0, 0) to (1, 1, 1) bounds:
- Lặp Lại (Repeat):
Repeat the image horizontally and vertically (tiling).
- Nới/Mở Rộng (Extend):
Extend the image by repeating the pixels on its edges.
- Cắt Xén/Đoạn Phim (Clip):
Cắt tới kích thước hình ảnh gốc và đặt toàn bộ các giá trị điểm ảnh bên ngoài thành màu đen trong suốt.
- Phản Chiếu Đối Xứng (Mirror):
Repeatedly flip the image horizontally and vertically.
- Nguồn (Source)
Type of image (Single Image, Movie...). See Các Sắp Đặt về Hình Ảnh (Image Settings).
- Số/Khung Hình (Frames)
How many frames of the Movie-type image (video) to play. Past this point, the video will be paused (unless Cyclic is enabled).
If you want to play the whole video, you can click Match Movie Length in the Image Editor's Sidebar, then copy the Frames from there to the node.
- Khung Hình Đầu (Start Frame)
Scene frame at which the video should start playing.
- Dịch Chuyển (Offset)
Number of frames to offset the video to an earlier point in time. (Put differently: how many frames at the start of the video to skip.)
Gợi ý
Blender plays video textures at the scene framerate, not their original framerate, meaning they'll be faster or slower than intended if these framerates don't match up. You can put a Driver on the Offset to work around this. Simply type the following into the field, replacing StartFrame, VideoFrameRate and SceneFrameRate by their respective numbers:
#(frame - StartFrame) * (VideoFrameRate - SceneFrameRate) / SceneFrameRate
- Cyclic (Tuần Hoàn)
Start over after the last frame to create a continuous loop.
- Tự Động Làm Tươi Mới Lại (Auto Refresh)
Update the video texture in the 3D Viewport when moving through the timeline.
- Color Space (Không Gian Màu Sắc)
The Color Space the image file was saved in. See Image Settings for details.
- Độ Đục (Alpha)
How the image uses its Alpha Channel. See Image Settings for details.
Đầu Ra (Outputs)¶
- Màu Sắc (Color)
RGB color from image. If the image has transparency, the color is premultiplied if the Alpha output is used, and unpremultiplied (straight) otherwise.
- Độ Đục (Alpha)
Kênh alpha từ hình ảnh.
Một Số Ví Dụ (Examples)¶

Image texture from GoodTextures.com.¶