Панель драйверов#
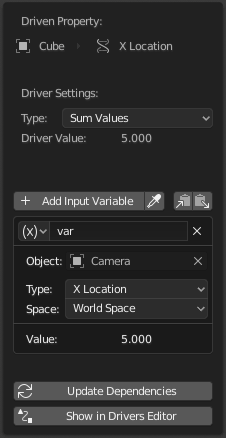
Всплывающее окно редактирования драйверов.#
Ссылка
- Редактор:
Graph editor
- Режим (mode):
Drivers
- Панель:
- Горячая клавиша:
N
Ссылка
- Меню:
- Горячая клавиша:
Ctrl-D
Эта панель отображается в боковой панели Редактор драйверов или в виде всплывающего окна при добавлении драйвера к свойству.
На ней отображается свойство драйвера, а затем ряд настроек, определяющих работу драйвера.
Driver Settings (Параметры драйвера)#
Тип (type)#
Существует две категории драйверов:
Встроенные функции (Average, Sum, Min и Max)
Управляемое свойство будет иметь значение среднего, суммы, наименьшего или наибольшего (соответственно) из значений ссылаемых переменных-драйверов. Если имеется только одна переменная-драйвер, эти функции дадут один и тот же результат.
Custom (Скриптовое выражение).
Произвольное выражение Python, которое может ссылаться на переменные драйвера по имени. См. раздел Expressions.
Driver Value (Значение драйвера)#
Текущий результат настройки драйвера. Полезно для отладки.
Variables (Переменные)#
См. Driver Variables.
Update Dependencies (Обновление зависимостей)#
Принудительное обновление зависимостей Значения драйвера.
Show in Drivers Editor (Отобразить в редакторе драйверов)#
Открывает полнофункциональный Редактор драйверов. Эта кнопка появляется только во всплывающей версии панели драйверов.
Driver Variables (Переменные драйвера)#
Переменные - это ссылки на свойства, каналы преобразования или результат сравнения преобразований двух объектов.
Для корректного отслеживания зависимостей драйверы должны обращаться к данным объекта через переменные драйвера, а не через прямые ссылки в выражении Python.

Кнопки Добавить, Копировать, Вставить.#
- Add Input Variable (Добавить входную переменную)
Добавляет новую переменную драйвера.
- Copy/Paste Variables (Копирование/Вставка переменных)
Копирует текущий список переменных, чтобы его можно было вставить в список переменных другого драйвера.
- Имя (name)
Имя для использования в скриптовых выражениях. Имя должно начинаться с буквы и содержать только буквы, цифры или символы подчеркивания.
- Variable Type (Тип переменной)
Тип используемой переменной.
- Single Property (Единственное свойство)
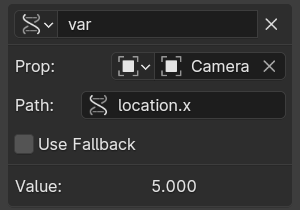
Получает значение свойства RNA, указанного ссылкой на блок данных и строкой пути.
В случае свойств трансформации это вернёт точное значение свойства UI, в то время как Transform Channel будет учитывать родительские и/или ограничивающие факторы по мере необходимости.
См. также Пользовательские свойства.
- ID Type (Тип ID)
Тип ID-блока. Например: Key, Image, Object, Material.
- ID
Идентификатор типа ID-блока. Например: «Material.001».
- RNA Path (Путь RNA)
The RNA name of the property, based on a subset of Python attribute access syntax. For example:
location.xorlocation[0]for the X location animation channel value (before parenting or constraints), or["prop_name"]for a custom property.- Fallback
If enabled, allows specifying a fallback value to use as the variable value if the RNA Path cannot be resolved, instead of causing a driver evaluation failure. For more info see Context Property below.
Совет
The easiest way to create a variable of this type is to use the Copy As New Driver context menu option of the input property, and paste the result into the driver via Paste Driver Variables.
- Transform Channel
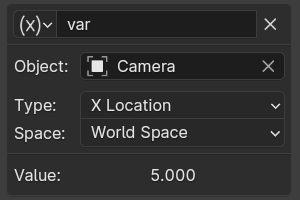
Retrieves the value of a Transform channel from an object or bone.
- ID
ID of the object. For example: Cube, Armature, Camera.
- Кость (bone)
For armatures, the name of the Armature bone. For example: «Bone», «Bone.002», «Arm.r».
- Тип (type)
For example, X Location, X Rotation, X Scale.
The Average Scale option retrieves the combined scale value, computed as the cubic root of the total change in volume. Unlike X/Y/Z Scale, this value can be negative if the object is flipped by negative scaling.
- Mode (Rotation)
For rotation channels, specifies the type of rotation data to use, including different explicit Euler orders. Defaults to using the Euler order of the target. See Rotation Channel Modes.
- Пространство (space)
World Space, Transform Space, Local Space.
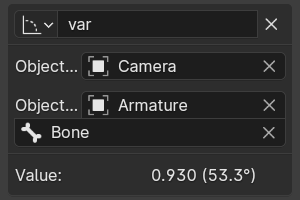
- Rotational Difference
Provides the value of the rotational difference between two objects or bones, in radians.
- Кость (bone)
For armatures, the name of the Armature bone. For example: «Bone», «Bone.002», «Arm.r».
- Расстояние (distance)
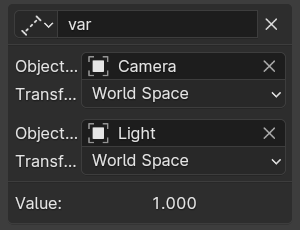
Provides the value of the distance between two objects or bones.
- Кость (bone)
For armatures, the name of the Armature bone. For example: «Bone», «Bone.002», «Arm.r».
- Пространство (space)
World Space, Transform Space, Local Space.
- Context Property
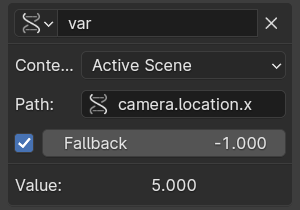
Provides the value of a property that is implicitly referring to either a scene or a view layer of the currently evaluating animation system. This is a weak reference which does not lead to the scene or view layer referenced from the driver to be linked when linking animation data.
An example when such properties comes in play is referring to a transformation of the active camera. It is possible to set up a driver in a character file, and make the driver use the set camera when the character is linked into a set.
- Контекст
Active Scene, Active View Layer.
- RNA Path (Путь RNA)
The RNA name of the property, based on a subset of Python attribute access syntax. For example:
camera.location.xorcamera.location[0]for the camera X location animation channel value (before parenting or constraints), or["prop_name"]for a custom property.- Fallback
If enabled, allows specifying a fallback value to use as the variable value if the RNA Path cannot be resolved, instead of causing a driver evaluation failure.
This feature can be very useful for making drivers more robust when implementing scene-global options using custom properties. When the object is linked into a different scene, these custom properties may not exist there, and the fallbacks can be used to provide sensible default values.
Fallbacks can also be used to emulate the lookup behavior of the View Layer mode of the material Attribute Node.
Совет
Although the values of the x/y/z animation channels for the camera location can be accessed via
camera.location[0/1/2], retrieving its world space location and orientation after parenting and constraints currently requires usingcamera.matrix_world. This property can be understood easily by viewing the matrix as an array of four vectors in World space:matrix_world[0][0/1/2]is the Screen Right direction vector (camera local X).matrix_world[1][0/1/2]is the Screen Up direction vector (camera local Y).matrix_world[2][0/1/2]is the opposite of the direction the camera is pointing.matrix_world[3][0/1/2]is the location of the camera.
- Значение (value)
Shows the value of the variable.
Rotation Channel Modes#
Rotation Transform Channels support a number of operation modes, including:
- Auto Euler
Uses the Euler order of the target to decompose rotation into channels.
- XYZ Euler, …
Explicitly specifies the Euler rotation order to use.
- Кватернион (quaternion)
Provides the Quaternion representation of the rotation.
- Swing and X/Y/Z Twist
Decomposes the rotation into two parts: a Swing rotation that aims the specified axis in its final direction, followed by a Twist rotation around that axis. This is often necessary for driving corrective Shape Keys and bones for organic joint rotation.
This decomposition is often produced in rigs by using a helper bone with a Damped Track Constraint to extract the swing part, and its child with Copy Transforms to extract the twist component.
The channels values for Swing and Y Twist are:
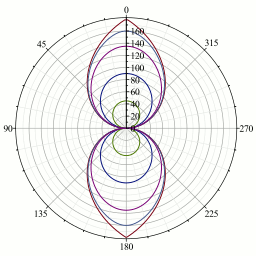
Falloff curves for weighted angles.#
- Y Rotation
True angle of the twist rotation.
- W Rotation
True angle of the swing rotation, independent of its direction.
- X Rotation, Z Rotation
Weighted angles that represent the amount of swing around the X/Z axis.
The magnitude of the angle equals W Rotation when the rotation is purely around that axis, and fades out to zero as the direction changes toward the other axis, following the falloff curves from the graph on the right.
Mathematically, the swing angles are computed from quaternion components, using \(2 \arccos(w)\) for W and \(2 \arcsin(x)\) etc. for the others. The component of the swing rotation that corresponds to the twist axis is always 0, and is replaced by the twist angle.
Выражения (expressions)#
- Expression
A text field where you can enter an arbitrary Python expression that refers to Driver Variables by their names.
The expression has access to a set of standard constants and math functions from
math,bl_mathand other modules, provided in the Driver Namespace. For an example of adding a custom function to the namespace, see the driver namespace example.For performance reasons it is best to use the Simple Expressions subset as much as possible.
- Use Self
If this option is enabled, the variable
selfcan be used for drivers to reference their own data. Useful for objects and bones to avoid having creating a Driver Variable pointing to itself.Example:
self.location.xapplied to the Y rotation property of the same object will make the object tumble when moving.Note that dependencies for properties accessed via
selfmay not be fully tracked.
Simple Expressions#
Blender can evaluate a useful subset of Python driver expressions directly, which significantly improves performance, especially on multi-core systems. To take advantage of this, the driver expression must only use the following features:
- Variable Names
Use only ASCII characters.
- Literals
Floating-point and decimal integer.
- Globals
frame- Constants
pi,True,False- Операторы
+,-,*,/,==,!=,<,<=,>,>=,and,or,not, conditional operator/ ternary if- Стандартные функции
min,max,radians,degrees,abs,fabs,floor,ceil,trunc,round,int,sin,cos,tan,asin,acos,atan,atan2,exp,log,sqrt,pow,fmod- Blender Provided Functions
lerp,clamp,smoothstep
Simple expressions are evaluated even when Python script execution is disabled.
When an expression outside of this subset is used, Blender displays a «Slow Python expression» warning. However, as long as the majority of drivers use simple expressions, using a complex expression in select few is OK.
См.также