Tính Chất (Properties)¶
Đường Cong-F đang Hoạt Động (Active F-Curve)¶
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Panel (Bảng):
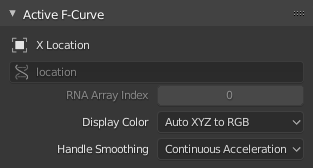
Bảng đường cong-F đang hoạt động.¶
Bảng này hiển thị các Tính Chất cho Đường Cong-F đang hoạt động.
- Tên Kênh (Channel Name)
The tên của tính chất that's hoạt họa bởi/theo the đường cong.
- Đường Dẫn Dữ Liệu (Data Path)
The programmatic đường đi/dẫn tới the tính chất.
- Chỉ Số Mảng RNA (RNA Array Index)
The index into the property, for multi-value properties. As an example, the Location property has three values (X, Y and Z), which means it can have three different curves with indices 0, 1 and 2.
- Màu Hiển Thị (Display Color)
Thế Nào/Phương Pháp tới determine the màu sắc của Đường Cong-F trong Đồ Thị trình biên soạn.
- Tự Động Cầu Vồng Hóa (Auto Rainbow)
Assigns a unique color to each curve that uses this setting.
- Tự Động XYZ Sang RGB (Auto XYZ to RGB)
Detects curves that animate an X/Y/Z coordinate and colors them red/green/blue accordingly.
- Người Dùng Định Nghĩa (User Defined)
Hãy you chọn the màu sắc yourself.
- Làm Mịn Tay Cầm (Handle Smoothing)
Thế Nào/Phương Pháp tới compute the Tay cầm bézier (Bézier handles) khi using the "Tự Động" hoặc "Tự Động Hạn Định" tay cầm
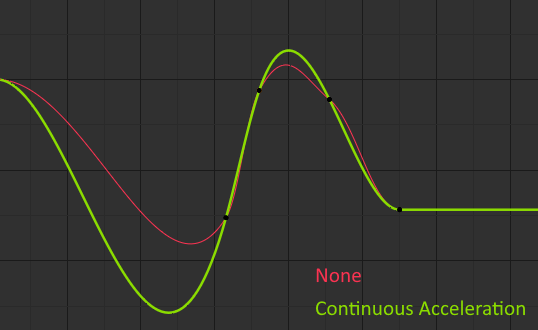
Xử lý so sánh chế độ làm mịn.¶
- Không (None)
Duy trực tiếp kề cạnh khóa giá trị sẽ được considered khi computing the tay cầm.
This older phương pháp được rất đơn giản và predictable, but it có thể duy produce truly làm mịn đường cong trong hầu hết trivial cases. Lưu Ý that the đỏ đường cong trong hình ảnh nằm trên has một few xoắn trong giữa.
- Tăng Tốc Liên Tục (Continuous Acceleration)
Một hệ thống của equations được solved vào/trong theo thứ tự tới tránh hoặc tối thiểu hóa jumps vào/trong tăng tốc tại every khung khóa.
Nó tạo ra các đường cong mượt mà hơn nhiều, song sự đòi hỏi cần thiết có nghĩa là bất kỳ thay đổi nào trong các giá trị của khóa có thể ảnh hưởng đến phép nội suy trên một đoạn đường cong đáng kể; mặc dù lượng thay đổi giảm dần theo cấp số nhân với khoảng cách. Quá trình lan truyền thay đổi này bị dừng lại bởi bất kỳ khóa nào có tay cầm "Phóng Thích/Thả/Tự Do/Miễn Phí", "Thẳng Hàng", hoặc "Véctơ", cũng như các phím cực trị có tay cầm "Tự Động Hạn Định".
The chế độ đồng thời tends tới cường điệu/quá mức/không kiềm chế và oscillate tăng với fully "Tự Động" tay cầm vào/trong some cases (xin xem hình ảnh nằm trên). So nó là recommended tới sử dụng "Tự Động Hạn Định" bởi/theo mặc định, và duy chuyển mạch tới "Tự Động" Tay Cầm vào/trong places where this được desired Hành Xử. That Hiệu Ứng có thể đồng thời be reduced bởi/theo Bổ Sung vào/trong-giữa Số Điểm Điều Khiển.
Mẹo
Xem xét các mặt tích cực và tiêu cực của mỗi chế độ, "Tăng Tốc Liên Tục" sẽ phù hợp hơn với hoạt họa ngắn, sử dụng một số lượng nhỏ các khóa nội suy với ít nhất công sức để trau truốt thủ công. Trong trường hợp hoạt họa đòi hỏi tính trau truốt cao với tỷ lệ khung khóa lớn, lợi ích của việc làm mịn có thể không còn giá trị hơn sự gián đoạn trong quy trình làm việc do sự lan truyền thay đổi xảy ra rộng lớn hơn.
Khung Khóa đang Hoạt Động (Active Keyframe)¶
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Panel (Bảng):
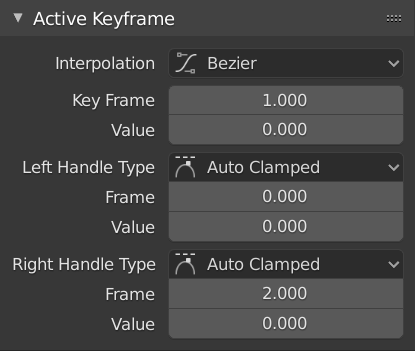
Bảng Khung Khóa đang hoạt động.¶
- Interpolation (Nội Suy)
The interpolation (nội suy) tới sử dụng giữa the khung khóa đang hoạt động và the tiếp theo.
Interpolation (Nội Suy)
- Hằng Số/Đồng Đều/Bất Biến (Constant):
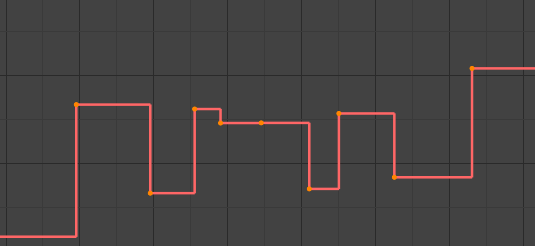
Hằng Số/Đồng Đều/Bất Biến.¶
The đường cong holds the giá trị until the khung khóa tiếp theo, producing một stair bước hiệu ứng với rất gián đoạn thay đổi. Bình Thường ra duy used during the khởi đầu "dàn cảnh" stage vào/trong tư thế-tới-tư thế hoạt họa quy trình làm việc.
- Tuyến Tính (Linear):
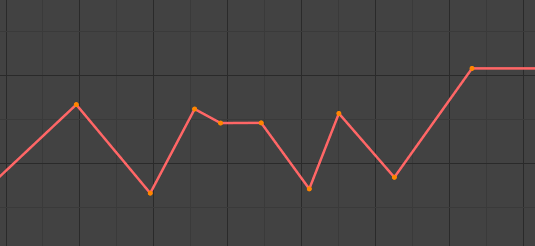
Tuyến Tính.¶
The curve goes from one keyframe to the next in a straight line, which prevents abrupt changes in value but not in speed. By creating two keyframes with Linear interpolation and extrapolation, you can easily make a straight line curve that goes on forever.
- Bézier (Đường Cong Bézier):
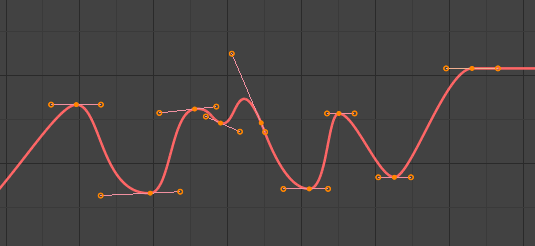
Bézier.¶
The default interpolation, which is smooth in both values and speed.
Ghi chú
F-Curves for properties that only accept discrete values will always have a stair step pattern, no matter which option you chose.
Chậm Rãi [theo cường độ] (Easing [by strength])
A set of interpolations that specialize in accelerating or decelerating an value, "easing" it from a stationary into a moving state or vice versa.
Xem thêm
Cho/đối với tăng thông tin và một few live demos, xin xem phương pháp suy giảm dần (easings.net) và Robert Penner's Chậm Rãi các Hàm (Robert Penner's Easing Functions).
Các Hiệu Ứng Năng Động (Dynamic Effects)
These additional easing types imitate (fake) physics-based effects like bouncing.
- Sau Lưng/Quay Trở Lại
With Ease In, the value first moves away from the target and then shoots towards it. With Ease Out, it goes towards the target, overshoots it, and then returns.
- Sau Lưng/Quay Trở Lại
The kích thước và chiều hướng (tức là, nằm trên/dưới the đường cong) của cường điệu/quá mức/không kiềm chế.
- Bật Nẩy (Bounce)
Makes the value bounce a few times with exponential decay, like a tennis ball that was dropped on the floor.
- Elastic (Đàn Hồi)
Makes the value overshoot the target, then rebound and undershoot it, then overshoot it again... with ever-decreasing intensity until it eventually settles.
- Biên Độ (Amplitude)
How far the value initially overshoots its target.
- Chu Kỳ (Period)
How much time there is between each oscillation.
- Chậm Rãi (Easing)
This option only applies to the Easing and Dynamic Effects categories above.
- Chậm Rãi Tự Động (Automatic Easing)
Automatically pick the most commonly used type: Ease In when using one of the Easing interpolations, and Ease Out when using one of the Dynamic Effects.
- Chậm Rãi Vào (Ease In)
The value accelerates, moving slowly at the beginning of the curve segment and speeding up towards the end.
- Chậm Rãi Ra (Ease Out)
The value decelerates, moving quickly at the beginning of the curve segment and slowing down towards the end.
- Chậm Rãi Vào Ra (Ease In Out)
The value moves slowly in the beginning, speeds up towards the middle, and slows down again towards the end.
- Khung Khóa (Key Frame)
The khung hình của khung khóa đang hoạt động.
- Value (Giá Trị)
The giá trị của khung khóa đang hoạt động.
- Kiểu Tay Cầm Trái / Phải (Left/Right Handle Type)
When the keyframe's interpolation is set to Bézier, the shape of the curve around it is influenced by its handles. Each handle has its own type which determines if (and how) Blender positions it automatically, and if not, how much freedom you have in positioning it manually.
You can change the handles' types in multiple ways: using these dropdowns in the Sidebar; through the menu ; or by pressing V and selecting from the popup menu.
If you want to change an automatic handle's position, just drag it; you don't need to manually change its type first.
- Tự Động (Automatic):

Các tay cầm tự động.¶
Tự Động tay cầm that produce làm mịn đường cong.
- Tự Động Hạn Định (Auto Clamped):

Các tay cầm hạn định.¶
Tay cầm tự động bị hạn định hòng để ngăn chặn những trường hợp không kiềm chế xảy ra và thay đổi chiều hướng của đường cong giữa các khung khóa (hình chữ-S).
- Véctơ (Vector):
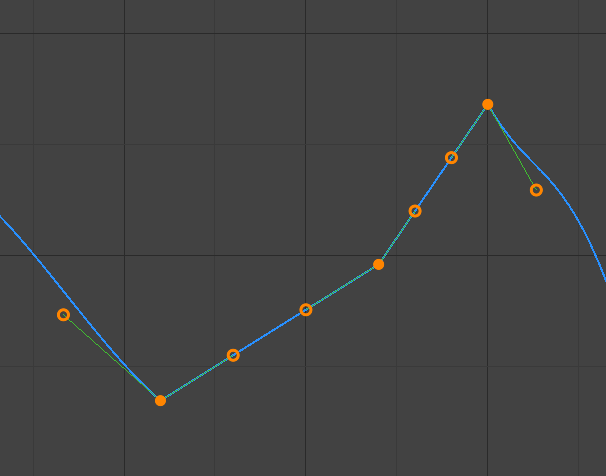
Các tay cầm Véctơ.¶
Tự Động tay cầm that produce thẳng đường cong số/phân đoạn (nội suy tuyến tính).
- Thẳng Hàng (Aligned):
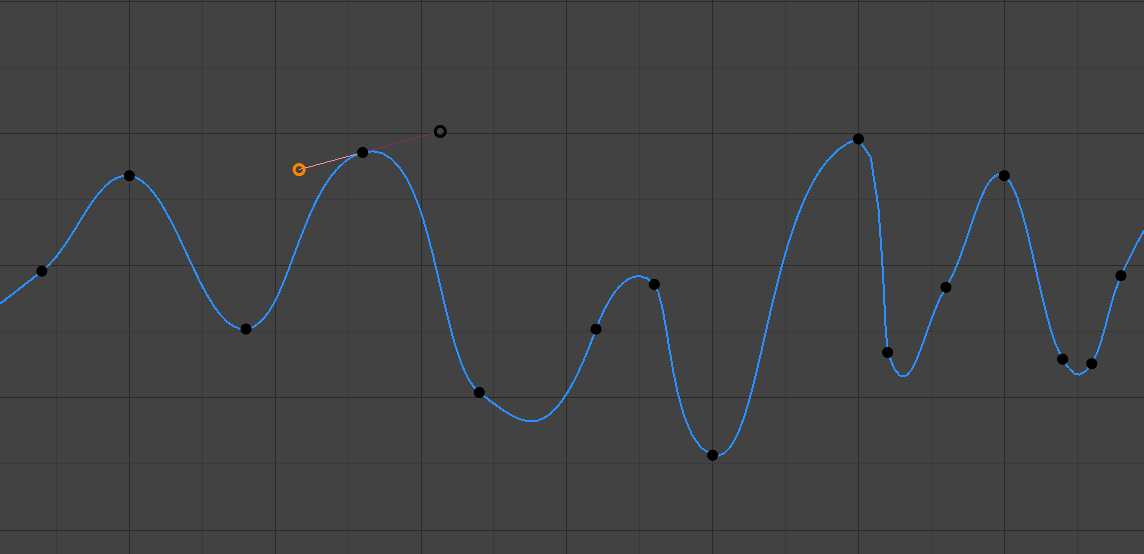
Các tay cầm thẳng hàng .¶
Thủ Công Tay Cầm, which sẽ được however bị Khóa Cùng nhau tới Luôn Luôn Điểm/Chấm vào/trong opposite directions. This results vào/trong một Đường Cong that được Luôn Luôn làm/Mịn Màng tại the Điểm Điều Khiển.
- Tự Do (Free):
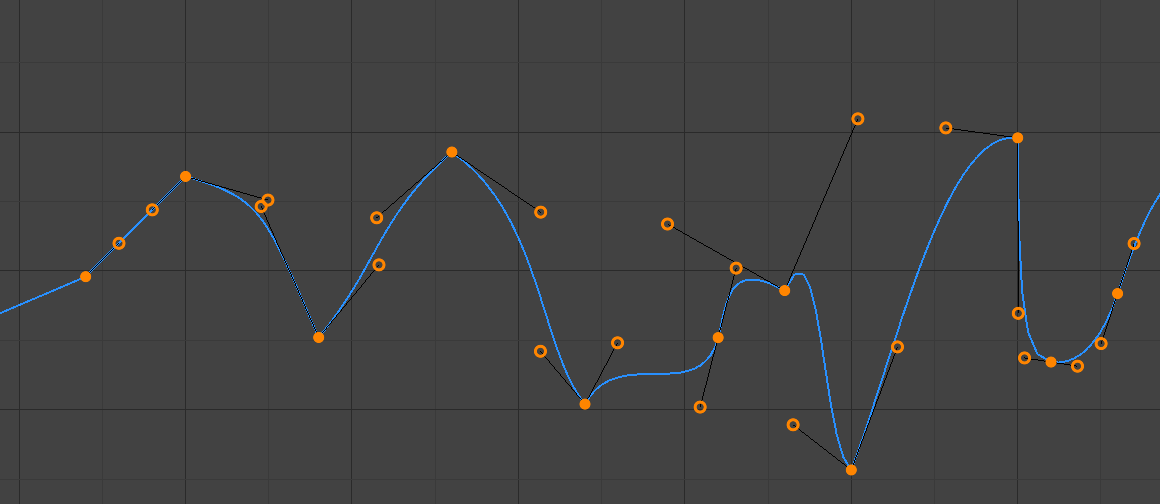
Các tay cầm tự do.¶
Thủ Công tay cầm that có thể be di chuyển một cách riêng biệt, và thus có thể kết quả vào/trong một sắc cạnh/đột ngột thay đổi của chiều hướng.
- Khung Hình, Giá Trị (Frame, Value)
The khung hình và giá trị cho/đối với the trái/tay cầm bên phải của khung khóa đang hoạt động.