Thuyên Chuyển Dữ Liệu của Khung Lưới (Transfer Mesh Data)¶
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Chế Độ (Mode):
Chế Độ Đối Tượng [Object Mode]
- Trình Đơn (Menu):
Transfer Mesh Data copies a certain type of data from the active mesh to the selected meshes. This could be UV maps, color attributes, custom normals, and so on.
For each element (vertex/edge/face) in each destination mesh, the operator finds one or more matching elements in the source mesh, then interpolates between those source elements' values.
The Điều Chỉnh Thao Tác Trước Đây (Adjust Last Operation) panel offers the following options.
- Ngưng Hoạt Động của Thao Tác (Freeze Operator)
Prevent changes to the settings from re-running the data transfer. This is useful if you are editing several settings at once with heavy geometry.
- Kiểu Dữ Liệu (Data Type)
Dữ liệu nào để thuyên chuyển sang.
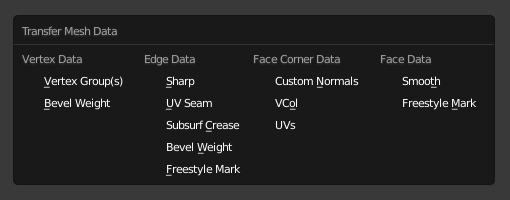
Kiểu dữ liệu.¶
- Kiến Tạo Dữ Liệu (Create Data)
Add any missing data layers on the destination meshes (e.g. create missing vertex groups).
- Ánh Xạ (Mapping)
How to find the matching source element(s) for each destination element. The various options are explained in the Mapping section below.
- Tự Động Biến Hóa (Auto Transform)
If the source and destination meshes don't overlap in world space, you can enable this option to calculate a transformation automatically. While this is quick and easy, however, you may get better results by making them overlap by hand.
- Biến Hóa Đối Tượng (Object Transform)
Whether take into account the world space transformations of the source and destination objects. When unchecked, the operator acts like all objects are in the same position and have the default rotation and scale.
- Duy Hình Học Lân Cận (Only Neighbor Geometry)
Only consider source elements that are close enough to the destination one.
- Khoảng Cách Tối Đa (Max Distance)
Khoảng cách tối đa cho phép giữa phần tử nguồn và phần tử đích (đối với ánh xạ phi cấu trúc liên kết).
- Bán Kính Tia Xạ (Ray Radius)
The starting radius to use when ray casting.
For certain mapping types, the operator performs a series of ray casts from each destination element to find matching source elements. These ray casts start with the specified radius and grow progressively larger until a match is found or a limit is reached.
A low starting radius will give more accurate results, but has worse performance if it's too small and needs to be increased. A high starting radius has better performance, but may result in suboptimal matches.
In general, use a low radius for dense source meshes and a high one for simple ones.
- Islands Precision
Controls the calculation that prevents a destination face from receiving UV coordinates from disparate source UV islands (areas bordered by seams). Keeping this at 0.0 means no island handling at all, while higher numbers increase the correctness of the result at the cost of extra computation.
Typically, small values like 0.02 are enough to get good results, but if you are mapping from a very high-poly source towards a very low-poly destination, you may have to raise it quite significantly.
- Lựa Chọn các Tầng Nguồn (Source Layers Selection)
Which source layers to copy to the destination meshes (e.g. only the active vertex group, all vertex groups, or a specific vertex group).
- Khớp với các Tầng Đích (Destination Layers Matching)
How to find the destination layer for a given source layer: by name or by order.
- Chế Độ Hòa Trộn (Mix Mode)
How to combine the new data from the source mesh with the original data in the destination meshes.
- Thay Thế (Replace)
Interpolate between the original and new value using Mix Factor.
- Trên Giới Hạn (Above Threshold)
Replace the destination value if it's greater than or equal to Mix Factor. In the case of multi-component data like colors, the threshold is compared to the average of these components.
For boolean Data Types like Freestyle Mark, you can use this to perform a logical AND: simply ensure the Mix Factor is 0.5 or greater, and the destination mesh will only have marked edges/faces that were already marked and are also marked in the source mesh.
- Giới Hạn Dưới (Below Threshold)
Replace the destination value if it's less than or equal to Mix Factor. In the case of multi-component data like colors, the threshold is compared to the average of these components.
For boolean Data Types like Freestyle Mark, you can use this to perform a logical OR: simply ensure the Mix Factor is 0.5 or greater, and the destination mesh will have marked edges/faces that were already marked or are marked in the source mesh.
- Hòa Trộn (Mix)
Mix the source value with the destination value, e.g. performing an alpha blend in the case of color attributes. Then, interpolate using Mix Factor.
- Thêm (Add)
Add the source value to the destination value, then interpolate using Mix Factor.
- Khấu Trừ (Subtract)
Subtract the source value from the destination value, then interpolate using Mix Factor.
- Nhân (Multiply)
Multiply the source value by the destination value, then interpolate using Mix Factor.
- Hệ Số Hòa Trộn (Mix Factor)
Interpolation factor between the original destination value and the newly calculated value. If Mix Mode is Above Threshold or Below Threshold, this is a threshold value instead.
Ánh Xạ (Mapping)¶
Topology (Cấu Trúc Liên Kết)¶
Simply matches the elements based on their index. This requires all meshes to have the same number of elements and those elements to be ordered in the same way. Best suited for a destination mesh that's a deformed copy of the source.
Xem thêm
Sắp Thứ Tự các Phần Tử (Sort Elements) to ensure the objects have the same element ordering.
Ánh Xạ Một-Đối-Một (One-To-One Mappings)¶
These mappings always select only one source element for each destination one.
- Dữ Liệu Điểm Đỉnh (Vertex Data)
- Đỉnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Vertex)
Use the nearest source vertex.
- Điểm Đỉnh của Cạnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Edge Vertex)
Use the nearest source vertex on the nearest (by midpoint distance) source edge.
- Điểm Đỉnh của Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Face Vertex)
Use the nearest source vertex on the nearest (by midpoint distance) source face.
- Dữ Liệu Cạnh (Edge Data)
- Điểm Đỉnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Vertices)
Use the source edge whose vertices are nearest to the destination edge's.
- Cạnh Gần Nhất (Nearest Edge)
Use the source edge whose midpoint is nearest to the destination edge's.
- Cạnh Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Face Edge)
Use the nearest source edge on the nearest face (both by midpoint distance).
- Face Corner Data
A face corner is a vertex in the context of a face. This concept is most commonly used in UV maps: each face corner can have its own UV coordinate, or in other words, one 3D vertex can correspond to several UV vertices (one per face).
- Góc Tối Cận cùng Pháp Tuyến Giống Nhất (Nearest Corner and Best Matching Normal)
Use the source corner that's nearest to the destination corner and has the most similar split normal.
- Góc Cạnh Gần Nhất và Pháp Tuyến Mặt Giống Nhất (Nearest Corner and Best Matching Face Normal)
Use the source corner that's nearest to the destination corner and has the most similar face normal.
- Góc Tối Cận của Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Corner of Nearest Face)
Use the nearest source corner on the nearest source face.
- Dữ Liệu Mặt (Face Data)
- Mặt Gần Nhất (Nearest Face)
Use the nearest source face (by midpoint distance).
- Pháp Tuyến Khớp Nhất (Best Normal-Matching)
Cast a ray from the destination face's centerpoint along the face's normal and use the source face found this way.
Ánh Xạ Nội Suy (Interpolated Mappings)¶
These mappings can match several source elements and interpolate between their values.
- Dữ Liệu Điểm Đỉnh (Vertex Data)
- Cạnh Gần Nhất được Nội Suy (Nearest Edge Interpolated)
Find the nearest point on the nearest source edge, then use that point to interpolate between the values of the edge's vertices.
- Mặt Gần Nhất được Nội Suy (Nearest Face Interpolated)
Find the nearest point on the nearest source face, then use that point to interpolate between the values of the face's vertices.
- Mặt Phóng Chiếu được Nội Suy (Projected Face Interpolated)
Project the destination vertex along its normal onto a source face, then use the projected point to interpolate between the values of the face's vertices.
- Dữ Liệu Cạnh (Edge Data)
- Cạnh Phóng Chiếu Nội Suy (Projected Edge Interpolated)
Find source edges by projecting from a number of points on the destination edge (where each point is projected along the interpolated normals of the destination edge's vertices). Then, interpolate between the values of the source edges found this way.
- Face Corner Data
- Mặt Gần Nhất được Nội Suy (Nearest Face Interpolated)
Find the nearest point on the nearest source face, then use that point to interpolate between the values of the face's corners.
- Mặt Phóng Chiếu được Nội Suy (Projected Face Interpolated)
Project the destination corner along its normal onto a source face, then use the projected point to interpolate between the values of the face's corners.
- Dữ Liệu Mặt (Face Data)
- Mặt Phóng Chiếu được Nội Suy (Projected Face Interpolated)
Find source faces by casting rays from a number of points on the destination face along the destination face's normal. Then, interpolate between the values of these source faces.