Kiến Tạo Lại Khung Lưới (Remeshing)¶
Blender offers several tools for regenerating a mesh so that it has (approximately) the same shape but fewer faces, more faces, or better topology.
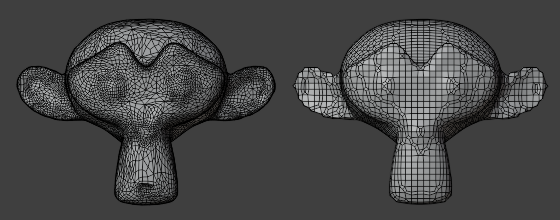
Remeshing to clean up messy geometry.¶
Kiến Tạo Lại Khung Lưới (Remeshing)¶
Tham Chiếu (Reference)
- Chế Độ (Mode):
Chế Độ Đối Tượng, Chế Độ Điêu Khắc (Object Mode, Sculpt Mode)
- Panel (Bảng):
Remeshing automatically rebuilds the mesh with a uniform topology. You can run it with a high resolution to make a simple mesh denser, making it more suitable for sculpting. Alternatively, you can run it with a low resolution to simplify and clean up overly dense or messy geometry, such as from a sculpt or a 3D scan.
Ghi chú
Remeshing only works on the original mesh data -- it ignores modifiers, shape keys and so on.
Remeshing is not possible on objects with a Bộ Điều Chỉnh Đa Phân Giải (Multiresolution Modifier).
The Remesh panel lets you choose between two different modes:
Voxel (Thể Tích Tử)¶
The Voxel remesher works by placing the mesh in a virtual 3D grid, seeing which points of the grid are closest to the mesh's outer surface, and generating a new mesh with vertices at those points. This means the resulting mesh has uniform topology and has no inner (self-intersecting) geometry.
It's useful for the following cases:
Changing the resolution of, or generally cleaning up, a mesh that you want to sculpt. Notably, by setting up the resolution before sculpting, you can leave Dyntopo disabled and avoid its performance impact.
Cleaning up a mesh for 3D printing.
Generating a simplified standin mesh for use with physics simulation.
However, because the topology is just a simple grid, the Voxel remesher should not be used for the following:
Creating topology for a mesh that will be deformed (e.g. a character that will be animated). Such topology has to follow the flow of the geometry, and no perfect automatic tools exist for this right now; it has to be done manually. See Retopology.
Generating a mesh for applying the Bộ Điều Chỉnh Bề Mặt Phân Hóa (Subdivision Surface Modifier) or the Bộ Điều Chỉnh Đa Phân Giải (Multiresolution Modifier). It's better to use the Quad (Tứ Giác) mode for this.
Reducing the face count of a mesh that otherwise has no problems with its geometry. It's better to use Tiêu Hao Hình Học (Decimate Geometry) for this.
Voxel remesh has the following settings:
- Kích Thước Thể Tích Tử (Voxel Size)
The size of each voxel (3D grid cell). Use a low value to get a detailed but dense mesh, or a high value for a light but coarse one.
- Tính Tùy Ứng (Adaptivity)
Reduces the final face count by simplifying geometry where detail is not needed. A value greater than zero disables Fix Poles and can introduce triangulation.
- Sửa Điểm Hội Tụ (Fix Poles)
Tries to reduce the number of Poles at the cost of some performance, to produce a better topological flow.
- Bảo Tồn (Preserve)
- Âm Lượng/Thể Tích (Volume)
Try to preserve the original volume of the mesh. Enabling this could make the operator slower depending on the complexity of the mesh.
- Thuộc Tính (Attributes)
Transfer attributes to the new mesh: the paint mask, any face sets, color attributes, and so on.
Xem thêm
The Bộ Điều Chỉnh Kiến Tạo Lại Khung Lưới (Remesh Modifier) can perform this operation non-destructively and offers more remeshing methods.
Quad (Tứ Giác)¶
The Quad remesher uses the Quadriflow algorithm, which can produce better results but is also slower. It's not a replacement for the Voxel remesher, however, because it doesn't clean up intersecting geometry.
It's useful for the following cases:
Generating a mesh for applying the Bộ Điều Chỉnh Bề Mặt Phân Hóa (Subdivision Surface Modifier) or the Bộ Điều Chỉnh Đa Phân Giải (Multiresolution Modifier).
However, it's not recommended for the following:
Cleaning up a mesh for sculpting or 3D printing. The Voxel remesher is more suited for this.
Creating final topology for a mesh that will be deformed (e.g. a character that will be animated). Such topology has to follow the flow of the geometry, and no perfect automatic tools exist for this right now; it has to be done manually. See Retopology.
Reducing the face count of a mesh that otherwise has no problems with its geometry. It's better to use Tiêu Hao Hình Học (Decimate Geometry) for this.
- Tứ Giác Hóa Khung Lưới (Quadriflow Remesh)
Opens a pop-up to set parameters for the remesh operation.
- Use Mesh Symmetry
Tạo khung lưới đối xứng bằng cách sử dụng các tùy chọn Đối Xứng Khung Lưới (Mesh Symmetry).
- Bảo Tồn Nét Sắc Nhọn (Preserve Sharp)
Try to preserve sharp features of the mesh. Enabling this could make the operator slower depending on the complexity of the mesh.
- Bảo Tồn Ranh Giới Khung Lưới (Preserve Mesh Boundary)
Try to preserve the original volume of the mesh. Enabling this could make the operator slower depending on the complexity of the mesh.
- Preserve Attributes
Transfer attributes to the new mesh: the paint mask, any face sets, color attributes, and so on.
- Làm Mịn Pháp Tuyến (Smooth Normals)
Apply Tô Bóng Mịn Màng (Shade Smooth) to the new mesh.
- Chế Độ (Mode)
Phương pháp để xác định lượng chi tiết cho khung lưới mới.
- Tỷ Số (Ratio):
Xác định số lượng các mặt mục tiêu tương đối với khung lưới hiện tại.
- Độ Dài Cạnh (Edge Length):
Specify target edge length in the new mesh.
- Các Mặt [Faces]:
Specify target number of faces in the new mesh.
- Seed (Mầm)
Seed (Mầm) ngẫu nhiên để sử dụng với trình giải nghiệm; các mầm khác nhau sẽ khiến trình kiến tạo lại khung lưới tạo ra các bố trí tứ giác khác nhau.
Tái Cấu Trúc Liên Kết (Retopology)¶
The automatic remesh tools generally don't result in topology that lends itself to deformation. Therefore, if you have sculpted a character and want to simplify it for animation, you'll typically have to do this manually in a process known as retopologizing.
To do this, you typically create a new mesh that overlaps the original one, then adjust it until it fully covers the original mesh and matches its shape.
The Tái Cấu Trúc Liên Kết (Retopology) overlay of the 3D Viewport is useful here, as it lets you see the original mesh through the retopologized one and vice versa -- without getting distracted by geometry on the other side as would be the case with X-Ray.
You can use the Dựng Đa Giác (Poly Build) tool to quickly add, change, and remove faces.
Use Bám Dính (Snapping) to align new vertices to the original mesh.