Modificador Booleana¶
El modificador Booleana permitirá combinar mallas usando una operación Booleana.
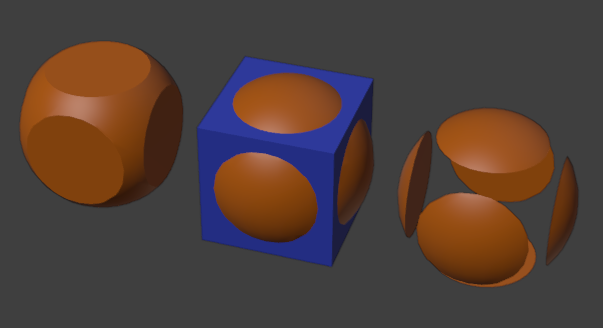
Aplicación del modificador a una esfera para crear una Intersección, Unión y Diferencia con un cubo. El cubo se encuentra oculto para facilitar la visualización.¶
Advertencia
Only Manifold meshes are guaranteed to give proper results. Non-manifold ones (especially meshes with holes) will usually work well, but might give odd glitches and artifacts. However, the Manifold Solver will not work at all on non-manifold meshes.
Truco
If you have marked your objects to show the edges (in , enable Wireframe), you will see the edge creation process while you are moving your objects around. You can also enable X-Ray to see inside the objects.
Ver también
Intersectar (Booleana) for performing one-off Boolean operations inside a mesh in Edit Mode.
Opciones¶
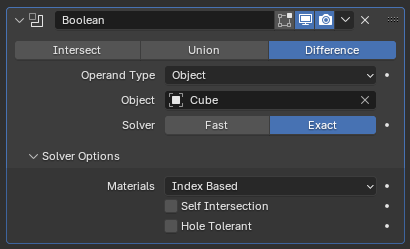
El modificador Booleana.¶
- Operación
- Intersección:
Sólo mantendrá el volumen interno de la malla modificada y todas las mallas del objeto de origen.
- Unión:
Agregará las mallas del objeto de origen a la malla modificada, eliminando cualquier cara interna.
- Diferencia:
Sustraerá las mallas del objeto de origen de la malla modificada.
- Tipo de operando
- Objeto:
El objeto de origen será un objeto de tipo malla individual.
- Colección:
El origen será una colección conteniendo cualquier número de objetos. En el caso de estarse usando el método Rápido, la operación Intersección no estará disponible.
- Objeto
El objeto (de tipo malla) de origen.
- Colección
The source collection. May be empty if Solver is Exact, in which case the modifier simply removes the modified mesh’s interior (self-intersecting) geometry.
- Método de resolución
Algoritmo utilizado para calcular la operación booleana.
- Rápido:
Uses a mathematically simple solver which offers the good performance; however, this solver lacks support for overlapping geometry.
- Exacto:
Uses a mathematically complex solver which offers the best results when there are coplanar faces or other overlapping geometry; however, this solver is much slower.
- Desplegable:
Uses a solver that is usually fastest but only works on manifold meshes, (plus the special case of Difference with a plane).
Opciones de cálculo¶
- Materiales método Exacto
Method for setting materials on the new faces.
- Basado en identificador:
Map the first material of the source mesh to the first material of the modified mesh, the second to the second, and so on. If a source face has a higher material index than the number of material slots on the modified mesh, the modified mesh’s first material is used.
- Transferir:
Use the same materials as on the source mesh, adding new material slots to the modified mesh as necessary. For empty slots, fall back to using the same material index as the source mesh.
- Intersección propia método Exacto
Correctly handle self-intersection in the participating meshes, at the cost of performance.
- Tolerancia a huecos método Exacto
Optimizes the Boolean output for Non-manifold geometry at the cost of increased computational time. Because of the performance impact, this option should only be enabled when the Exact solver demonstrates errors with non-manifold geometry.
- Umbral de superposición método Rápido
Maximum distance between two faces to consider them as overlapping. This helps solve the limitation of this solver. If the result is still not as expected, try using the Exact solver.